The emergence of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) has sparked a transformative shift in the digital art market, offering artists unprecedented avenues for monetization and collectors innovative means to own and trade digital assets. This disruptive technology has reshaped traditional notions of ownership and value, opening up a world of possibilities for creators and investors alike. However, along with the immense opportunities presented by the NFT boom come distinct challenges, particularly in the realm of contract drafting and management. As the digital art market continues to evolve at a rapid pace, it becomes increasingly crucial to navigate the complexities of NFT contracts effectively to ensure both security and scalability.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of NFT contracts, exploring key considerations and best practices to safeguard the interests of all stakeholders in this dynamic and evolving landscape of digital creativity and commerce.
Understanding NFT Contracts
NFT contracts play a pivotal role in facilitating transactions involving digital assets represented by Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). These contracts establish the legal framework governing the sale, transfer of ownership, and associated rights and obligations. In the context of the digital art market, NFT contract management delineates crucial details such as ownership rights, royalties, licensing terms, and any conditions or restrictions about the use or reproduction of digital artwork.
Given the unique characteristics of NFTs and the digital nature of the assets involved, contract drafting must address specific considerations to safeguard the interests of both artists and collectors. These considerations may include aspects related to intellectual property rights, digital licensing, authentication mechanisms, resale rights, and provisions for dispute resolution. By carefully crafting NFT contracts that address these nuanced issues, parties can ensure clarity, transparency, and legal enforceability in their transactions within the dynamic landscape of the digital art market.
Ensuring Security in Contract Drafting
Security is of paramount importance in the drafting of NFT contracts, particularly given the digital nature of the assets involved and the potential for high-value transactions. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are frequently utilized in NFT transactions due to their efficiency and transparency. Powered by blockchain technology, smart contract management offers an unprecedented level of security by providing immutability and automated execution, thereby minimizing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
However, while smart contracts offer robust security features, it is essential to ensure that the underlying code is meticulously audited to identify and rectify any vulnerabilities. This auditing process involves a comprehensive review of the smart contract code by experienced developers and cybersecurity experts to uncover potential weaknesses or loopholes that could be exploited by malicious actors. By conducting thorough audits and implementing rigorous security measures, stakeholders can bolster the integrity and reliability of NFT contracts, thereby safeguarding the interests of all parties involved in the digital art market.
Addressing Ownership Rights and Licensing
One critical aspect of NFT contracts involves clearly defining ownership rights and licensing terms. Artists maintain copyright ownership of their work, even after it has been tokenized as an NFT. However, collectors acquire ownership of the token itself, which represents the digital asset. Therefore, it is imperative that contract drafting delineates these rights, outlining the specific ownership rights granted to collectors and the corresponding licensing terms for the use of digital artwork.
In addition to specifying ownership rights and licensing terms, NFT contracts may also address issues such as royalties and resale rights. Artists may include provisions detailing the percentage of proceeds they are entitled to receive from secondary sales of their NFTs, known as royalties. Likewise, collectors may seek assurances regarding their ability to resell NFTs and whether any resale royalties are applicable. By incorporating these provisions into the contract drafting process, artists and collectors can establish clear guidelines for the monetization and distribution of digital assets, ensuring fairness and transparency in the digital art market.
Implementing Royalty Mechanisms
The rise of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) has ushered in a new era for the digital art market, offering artists unprecedented opportunities to monetize their creations and collectors novel ways to own digital assets. However, this burgeoning industry also presents unique challenges, particularly in terms of contract drafting and management. NFT contracts serve as the legal backbone of transactions involving digital assets represented by NFTs, defining crucial terms such as ownership rights, royalties, and licensing terms. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of NFT contracts, focusing on the incorporation of royalty mechanisms.
We explore how these mechanisms, embedded within smart contracts, ensure that artists receive fair compensation for secondary sales of their work, fostering a more equitable and sustainable ecosystem for creators and collectors alike.
- Royalty Mechanisms: NFT contracts often include royalty mechanisms to ensure that artists receive compensation for secondary sales of their work. These mechanisms can be embedded into smart contracts, which are programmable and automatically execute predefined actions based on predefined conditions.
- Automatic Distribution: Smart contracts can be programmed to automatically distribute royalties to artists each time their NFT is resold on a secondary market. This feature eliminates the need for manual tracking and payment processing, streamlining the royalty distribution process and ensuring timely compensation for artists.
- Incentivizing Artists: By guaranteeing royalties for secondary sales, NFT contracts incentivize artists to participate in the digital art market and create more works for tokenization. This financial incentive encourages artists to embrace NFT technology and explore new opportunities for monetizing their creative output.
- Equitable Ecosystem: Implementing royalty mechanisms in NFT contracts contributes to building a more equitable and sustainable ecosystem for creators. It ensures that artists continue to benefit from the appreciation of their work over time, even as it changes hands on secondary markets.
- Transparency and Accountability: NFT contracts with built-in royalty mechanisms enhance transparency and accountability in the digital art market. Artists and collectors can rely on the immutability and transparency of blockchain technology to verify royalty payments and track the resale history of NFTs, fostering trust and confidence in the ecosystem.
- Scalability in Contract Management: As the popularity of NFTs continues to soar, scalability becomes a critical factor in contract management. With potentially thousands of transactions occurring daily on NFT marketplaces, contract management systems must be capable of handling large volumes of data efficiently. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and accessibility, allowing stakeholders to manage contract management seamlessly across multiple platforms.
Integrating Legal Compliance Measures
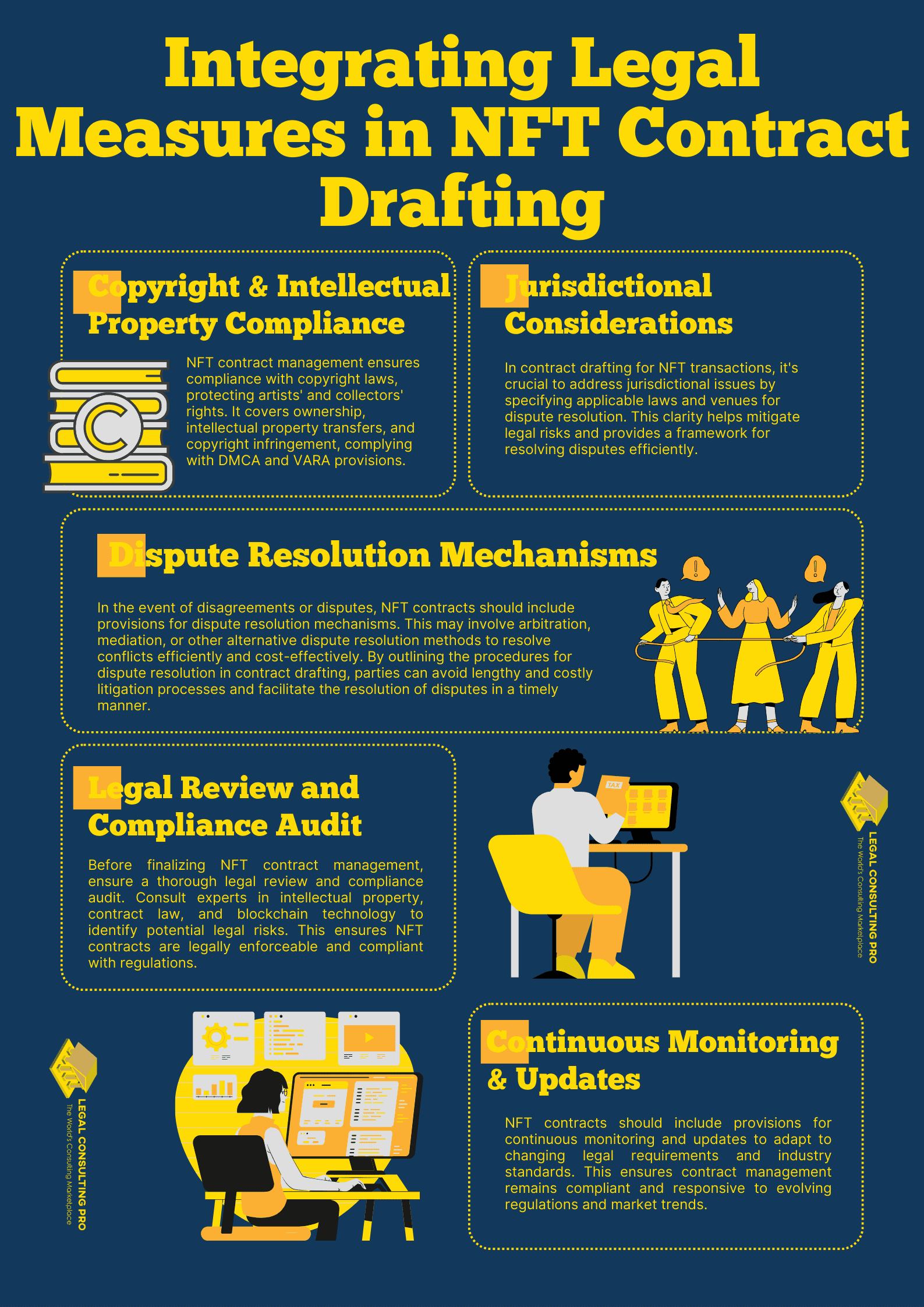
- Copyright and Intellectual Property Compliance: NFT contract management must adhere to copyright and intellectual property laws to protect the rights of both artists and collectors. Provisions should be included in contract drafting to ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and the Visual Artists Rights Act (VARA). These provisions may outline the ownership rights of artists, the transfer of intellectual property rights to collectors, and mechanisms for addressing copyright infringement.
- Jurisdictional Considerations: Contract drafting should also address jurisdictional issues to determine which laws govern the NFT transaction in case of legal disputes. This involves specifying the applicable jurisdiction and venue for resolving disputes, which may vary depending on the parties involved and the nature of the transaction. By clarifying jurisdictional considerations upfront, NFT contracts can mitigate legal risks and provide clarity in the event of disputes.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: In the event of disagreements or disputes, NFT contracts should include provisions for dispute resolution mechanisms. This may involve arbitration, mediation, or other alternative dispute resolution methods to resolve conflicts efficiently and cost-effectively. By outlining the procedures for dispute resolution in contract drafting, parties can avoid lengthy and costly litigation processes and facilitate the resolution of disputes promptly.
- Legal Review and Compliance Audit: Before finalizing NFT contract management, it’s essential to conduct a thorough legal review and compliance audit to ensure that all provisions comply with applicable laws and regulations. This may involve consulting with legal experts specializing in intellectual property, contract law, and blockchain technology to identify any potential legal risks or compliance issues. By conducting a comprehensive legal review, parties can mitigate legal risks and ensure that their NFT contracts are legally enforceable and compliant with relevant regulations.
- Continuous Monitoring and Updates: Finally, NFT contracts should include provisions for continuous monitoring and updates to adapt to evolving legal requirements and industry standards. The digital art market and regulatory landscape are constantly evolving, requiring parties to stay informed about changes that may impact their NFT transactions. By incorporating provisions for continuous monitoring and updates, NFT contract management can remain legally compliant and responsive to changes in the legal and regulatory environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the NFT boom represents a significant milestone in the evolution of the digital art market, offering unprecedented opportunities for artists, collectors, and enthusiasts. However, along with these opportunities come unique challenges, particularly in terms of contract drafting and management. By prioritizing secure and scalable contract drafting practices, stakeholders can effectively navigate the complexities of the NFT landscape while mitigating risks and maximizing benefits.
With a focus on security measures, clear delineation of ownership rights, scalability to accommodate growing demand and adherence to legal compliance requirements, NFT contracts can serve as robust frameworks for facilitating transactions and fostering trust in the digital art ecosystem. Ultimately, by embracing these principles, stakeholders can harness the full potential of NFTs to revolutionize the art industry and shape the future of digital creativity.
Similar blogs related to contract drafting:
Contract Drafting: Sustainable Supply Chains: Incorporating Environmental and Social Responsibility
Contract Drafting: ESG in Action: Weaving Sustainability Clauses