In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the environmental and social impacts of supply chain operations. As a result, businesses are increasingly focusing on sustainability initiatives to minimize their carbon footprint, promote ethical labor practices, and contribute positively to society. One effective way to embed environmental and social responsibility into supply chain operations is through contract drafting and contract management. This article explores the role of contract drafting and management in fostering sustainable supply chains, highlighting key strategies and best practices for integrating environmental and social considerations into contract drafting.
Understanding Sustainable Supply Chains
Understanding Sustainable Supply Chains entails grasping the concept of ensuring that products and services are sourced, produced, and delivered in a manner that minimizes environmental impact, respects social equity, and promotes economic viability throughout the supply chain.
Definition of Sustainable Supply Chains
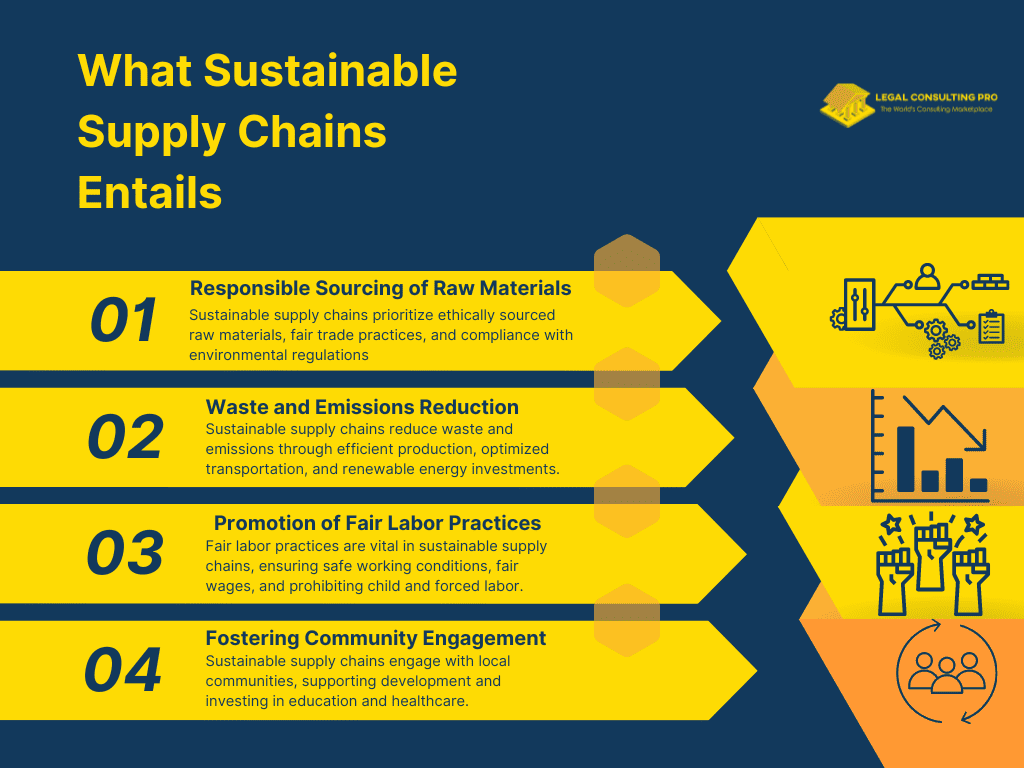
Sustainable supply chains encompass a holistic approach to managing various processes within the production and distribution of goods and services. The focus extends beyond mere profitability to include environmental, social, and economic factors. Here’s a breakdown of what this entails:
- Responsible Sourcing of Raw Materials: Sustainable supply chains prioritize the sourcing of raw materials from suppliers that adhere to ethical and sustainable practices. This may involve sourcing materials from certified sustainable sources, promoting fair trade practices, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Waste and Emissions Reduction: Sustainable supply chains aim to minimize waste generation and emissions throughout the production and distribution process. This may involve implementing efficient production methods, optimizing transportation routes to reduce fuel consumption, and investing in renewable energy sources to reduce carbon emissions.
- Promotion of Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring fair labor practices is a key component of sustainable supply chains. This includes providing safe working conditions, fair wages, and benefits to workers, as well as prohibiting the use of child labor and forced labor in the supply chain.
- Fostering Community Engagement: Sustainable supply chains actively engage with local communities to understand their needs and concerns, and to contribute positively to their development. This may involve supporting community development projects, providing job opportunities, and investing in education and healthcare initiatives.
By integrating these principles into supply chain management practices, businesses can create more sustainable and resilient supply chains that benefit both the environment and society while also ensuring long-term economic viability.
Importance of Sustainability in Modern Business Practices
Sustainability has emerged as a fundamental aspect of contemporary business operations, driven by a confluence of factors such as environmental degradation, social inequality, and resource scarcity. Here’s how the adoption of sustainable supply chain practices addresses these concerns and yields various benefits for businesses:
- Mitigating Risks: Sustainable supply chain practices help mitigate risks associated with environmental degradation, such as climate change impacts, resource depletion, and pollution. By implementing measures to reduce carbon emissions, conserve resources, and minimize waste, businesses can build resilience against the adverse effects of environmental disruptions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with environmental regulations is increasingly stringent, and businesses must adhere to these requirements to avoid penalties and legal liabilities. Sustainable supply chain practices help companies meet regulatory standards related to environmental protection, worker safety, and product quality, ensuring long-term compliance and avoiding reputational damage.
- Enhancing Brand Reputation: Consumers are becoming more socially and environmentally conscious, and they favor businesses that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Adopting sustainable supply chain practices enhances brand reputation by signaling to customers that a company is socially responsible, environmentally conscious, and ethical in its operations. This positive brand image can lead to increased customer loyalty, trust, and market competitiveness.
- Attracting Environmentally Conscious Consumers: As awareness of environmental issues grows, consumers are increasingly seeking products and services from companies that prioritize sustainability. By aligning with consumer values and preferences, businesses that embrace sustainable supply chain practices can attract environmentally conscious consumers and tap into a growing market segment.
- Driving Innovation: Sustainability challenges present opportunities for innovation and differentiation in the marketplace. Companies that invest in sustainable supply chain practices often discover new technologies, processes, and business models that lead to cost savings, efficiency improvements, and competitive advantages. By fostering a culture of innovation, sustainable supply chains drive continuous improvement and long-term business success.
Environmental and Social Challenges in Traditional Supply Chains
Traditional supply chains often face significant environmental and social challenges, including:
- Pollution and Resource Depletion: Extraction of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and transportation contribute to pollution, deforestation, habitat destruction, and depletion of natural resources.
- Labor Exploitation: Labor abuses such as child labor, forced labor, unsafe working conditions, and low wages are prevalent in many industries, particularly in developing countries.
- Lack of Transparency: Complex and opaque supply chains make it difficult for companies and consumers to trace the origins of products, assess environmental and social impacts, and hold supply chain actors accountable.
- Economic Inequality: Unequal distribution of economic benefits along the supply chain perpetuates poverty, marginalization, and social unrest, particularly in vulnerable communities.
The Role of Contract Drafting in Sustainable Supply Chain Management
Introduction to Contract Drafting in Supply Chain Management:
Contract drafting serves as the foundation for establishing legal agreements between various stakeholders involved in the supply chain. These contracts outline the terms, conditions, rights, and responsibilities of each party, providing clarity and structure to business relationships.
In the context of sustainable supply chain management, contract drafting plays a crucial role in formalizing commitments to environmental and social responsibility. By incorporating sustainability clauses into contract drafting, organizations can ensure that ethical and sustainable practices are upheld throughout the supply chain.
Incorporating Environmental and Social Responsibility Clauses into Contract Drafting
Environmental and social responsibility clauses are provisions within contracts that outline commitments to sustainable practices. These clauses are designed to address environmental impacts, promote fair labor practices, and uphold ethical standards throughout the supply chain.
During contract drafting, organizations can include specific language that requires suppliers and partners to comply with environmental regulations, adhere to fair labor standards, and engage in ethical sourcing practices. These clauses establish clear expectations and standards for all parties involved, fostering accountability and transparency.
Examples of Sustainability Clauses:
Environmental Performance Standards: Contracts may include clauses that establish environmental performance standards, such as targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and waste generation. These standards help organizations measure and track their environmental impact, driving continuous improvement in sustainability practices.
Fair Labor Practices: Sustainability clauses can also address fair labor practices, requiring suppliers to provide safe working conditions, fair wages, and nondiscriminatory employment practices. These clauses may prohibit the use of child labor, forced labor, and other exploitative practices, ensuring that workers are treated ethically and respectfully.
Ethical Sourcing Requirements: Contract drafting may incorporate clauses that mandate ethical sourcing practices, such as requirements for transparency and traceability in the supply chain. These clauses ensure that suppliers source materials and products responsibly, avoiding unethical practices such as the use of conflict minerals or involvement in illegal logging.
Ensuring Legal Compliance and Enforceability of Sustainability Clauses:
Contract drafting professionals must ensure that sustainability clauses comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This may involve conducting thorough legal research, consulting with legal experts, and incorporating language that addresses legal requirements and potential liabilities.
Sustainability clauses must be practical, measurable, and enforceable in practice. Organizations should establish mechanisms for monitoring and enforcing compliance with these clauses, such as audits, inspections, and performance reviews. Additionally, contract drafting may include provisions for remediation in the event of non-compliance, outlining steps for addressing violations, and resolving disputes.
In conclusion, contract drafting plays a vital role in promoting sustainability in supply chain management by incorporating environmental and social responsibility clauses into -. These clauses establish clear expectations and standards for sustainable practices, fostering accountability and transparency throughout the supply chain. However, ensuring the legal compliance and enforceability of sustainability clauses requires careful consideration of legal requirements, industry standards, and practical considerations. By integrating sustainability into contract drafting processes, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to ethical and sustainable business practices, driving positive change in the global supply chain.

Leveraging Contract Management for Sustainability:
Overview of Contract Management Processes and Tools:
Contract management involves the administration and oversight of contracts throughout their lifecycle, from creation and negotiation to execution and renewal. It encompasses various processes, including contract drafting, approval, storage, and analysis.
Contract management tools, such as contract lifecycle management (CLM) software, help organizations streamline and automate contract-related tasks. These tools centralize contract data, facilitate collaboration among stakeholders, and ensure compliance with contractual obligations.
Tracking and Monitoring Environmental and Social Performance Metrics:
Contract management systems can be leveraged to track and monitor environmental and social performance metrics outlined in sustainability clauses. By integrating sustainability criteria into contract templates and workflows, organizations can capture relevant data and monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) throughout the contract lifecycle.
For example, organizations may track metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, waste generation, and labor practices to assess suppliers’ adherence to sustainability commitments. Contract management tools enable organizations to collect, analyze, and report on these metrics to stakeholders and regulatory authorities.
Implementing Supplier Performance Evaluations and Audits:
Contract management systems facilitate supplier performance evaluations and audits to assess compliance with sustainability requirements. Organizations can establish criteria for evaluating suppliers’ environmental and social performance and conduct regular assessments to ensure alignment with contractual obligations.
Supplier scorecards and performance dashboards within contract management tools provide visibility into supplier performance metrics, allowing organizations to identify areas for improvement and recognize top-performing suppliers. Audits and inspections can be scheduled and managed within the contract management system, ensuring thorough assessments of suppliers’ sustainability practices.
Addressing Non-Compliance and Remediation Through Contract Management:
Contract management systems play a critical role in addressing non-compliance and facilitating remediation efforts. When deviations from sustainability clauses are identified, organizations can initiate corrective actions and remediation plans through the contract management platform.
For instance, contract management tools enable organizations to document non-compliance incidents, track corrective actions, and monitor progress toward resolution. Automated notifications and alerts can notify stakeholders of non-compliance events and upcoming deadlines, ensuring timely response and accountability.
Additionally, contract management systems provide a centralized repository for storing documentation related to non-compliance incidents, including correspondence, audit reports, and remediation plans. This documentation can be crucial for demonstrating efforts to address non-compliance and mitigate risks associated with sustainability breaches.
Best Practices for Sustainable Contracting
Best practices for sustainable contracting involve collaboration among legal, procurement, and sustainability teams, engaging with suppliers to align on sustainability goals and expectations, incorporating sustainability criteria into supplier selection and evaluation processes, and regularly reviewing and updating sustainability clauses to reflect evolving standards and regulations. By adopting these best practices, organizations can promote sustainability throughout the supply chain, drive positive environmental and social impact, and build resilient and responsible supply chains for the future.
Collaboration between Legal, Procurement, and Sustainability Teams:
Effective sustainable contracting begins with collaboration among legal, procurement, and sustainability teams. By bringing together these diverse stakeholders, organizations can ensure that sustainability considerations are integrated into all stages of the contracting process. Legal teams provide expertise in contract drafting, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations, while procurement teams focus on supplier relationships and procurement strategies. Sustainability teams contribute knowledge of environmental and social issues, as well as expertise in setting sustainability goals and metrics. Collaboration among these teams facilitates the development of comprehensive and effective sustainable contracting practices.
Engaging with Suppliers to Align on Sustainability Goals and Expectations:
Engaging with suppliers is essential for aligning sustainability goals and expectations. Organizations should communicate their commitment to sustainability and encourage suppliers to share their sustainability initiatives and practices. This dialogue helps build trust and collaboration between buyers and suppliers, fostering a shared commitment to sustainability throughout the supply chain. Through regular communication and collaboration, organizations can work with suppliers to identify areas for improvement and develop joint sustainability initiatives.
Incorporating Sustainability Criteria into Supplier Selection and Evaluation Processes:
When selecting suppliers, organizations should prioritize sustainability criteria alongside traditional factors such as cost, quality, and reliability. This involves assessing suppliers based on their environmental performance, social responsibility, and commitment to sustainability. Organizations can use sustainability scorecards, questionnaires, and audits to evaluate suppliers’ sustainability practices and performance. By incorporating sustainability criteria into supplier selection processes, organizations can ensure that they work with suppliers who share their commitment to sustainability and ethical business practices.
Regular Review and Updating of Sustainability Clauses:
Sustainability clauses within contracts should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving standards and regulations. As sustainability practices and expectations change over time, organizations must ensure that their contract drafting remains current and relevant. Legal teams should conduct periodic reviews of existing contracts to assess the effectiveness of sustainability clauses and identify opportunities for improvement. Additionally, legal teams should stay informed about changes in sustainability standards, regulations, and industry best practices to ensure that contracts reflect the latest requirements.
Monitoring and Enforcement of Sustainability Clauses:
Once contracts are in place, organizations must monitor and enforce sustainability clauses to ensure compliance. This involves tracking suppliers’ performance against sustainability metrics, conducting regular audits and inspections, and addressing any instances of non-compliance promptly and effectively. Organizations can use contract management systems and tools to automate monitoring and enforcement processes, facilitating timely intervention and remediation when necessary.
Supplier Engagement and Collaboration:
Building strong relationships with suppliers is key to promoting sustainability throughout the supply chain. Organizations should engage with suppliers regularly to discuss sustainability goals, share best practices, and identify opportunities for collaboration. By working together, organizations and suppliers can develop innovative solutions to sustainability challenges and drive continuous improvement in environmental and social performance.
Transparency and Reporting:
Transparency is essential for fostering trust and accountability in sustainable contracting. Organizations should be transparent about their sustainability goals, initiatives, and performance, both internally and externally. This includes disclosing information about sustainability practices in procurement processes, sharing sustainability reports with stakeholders, and engaging in dialogue with customers, investors, and other stakeholders about sustainability issues.
Continuous Improvement and Learning:
Sustainable contracting is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and learning. Organizations should regularly evaluate their sustainable contracting practices, seek feedback from stakeholders, and identify opportunities for innovation and improvement. By continuously learning and adapting, organizations can stay ahead of emerging sustainability trends and challenges, driving positive change in the supply chain.

Case Studies and Examples:
Implementing Sustainability Clauses in Supplier Contracts:
- A global manufacturer recognized the significance of sustainability in its supply chain and integrated environmental and social responsibility clauses into its supplier contracts.
- Through collaboration among legal, procurement, and sustainability teams, a set of sustainability criteria was developed and incorporated into supplier selection and evaluation processes.
- By engaging with suppliers and enforcing sustainability clauses, notable improvements in supplier sustainability practices were achieved.
Updating Sustainability Clauses in Response to Regulatory Changes:
- A leading retailer faced regulatory changes impacting its sustainability obligations and sought to update its contract templates accordingly.
- Legal teams conducted a thorough review of existing contract drafting, identifying outdated or non-compliant sustainability clauses and developing revised templates.
- Through proactive communication with suppliers and comprehensive training for procurement teams, updated sustainability clauses were successfully implemented.
Leveraging Technology for Sustainable Contract Management:
- A multinational corporation recognized the need for more efficient contract management practices to support its sustainability goals.
- By investing in contract management software with sustainability features, automated contract drafting, monitoring, and enforcement processes were implemented.
- Through data analytics and reporting tools, insights into supplier performance were gained, facilitating continuous improvement in sustainability practices.
Key Takeaways:
- Cross-functional collaboration is essential for the successful implementation of sustainable contracting practices.
- Regular review and updating of sustainability clauses are necessary to ensure compliance with evolving standards and regulations.
- Transparency, communication, and engagement with suppliers are critical for promoting sustainability throughout the supply chain.
- Leveraging technology can enhance efficiency, transparency, and accountability in sustainable contract management.
In conclusion, these case studies illustrate effective strategies for implementing sustainable supply chain practices through contract drafting and management. By integrating sustainability clauses, staying abreast of regulatory changes, and leveraging technology, organizations can drive positive environmental and social impact in their supply chains.
Challenges and Future Trends in Sustainable Contracting:
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority for businesses worldwide as they recognize the importance of integrating environmental and social responsibility into their supply chain operations. However, incorporating sustainability into supply chain contract drafting comes with its own set of challenges and complexities. Identifying and addressing these challenges is crucial for organizations to effectively navigate the evolving landscape of sustainable contracting.
Identifying Common Challenges:
- Lack of Standardization: One of the primary challenges in sustainable contracting is the absence of standardized sustainability criteria and metrics. Without uniform guidelines, organizations may struggle to align sustainability requirements in contracts, leading to ambiguity and inconsistency in implementation.
- Complexity of Supply Chains: Supply chains are inherently complex, involving multiple tiers of suppliers and subcontractors across various geographic locations. Managing sustainability across these diverse networks can be challenging, as organizations may face difficulties in tracking and monitoring sustainability performance throughout the supply chain.
- Resistance to Change: Resistance to change from suppliers is another common challenge in sustainable contracting. Some suppliers may be hesitant to adopt sustainability practices due to perceived costs, operational disruptions, or lack of awareness. Overcoming this resistance and fostering buy-in from suppliers is essential for successfully integrating sustainability into supply chain contract drafting.
- Limited Transparency: Limited transparency into suppliers’ operations and practices poses a significant challenge in sustainable contracting. Without access to accurate and timely data, organizations may struggle to assess and verify compliance with sustainability requirements, hindering efforts to enforce contractual obligations effectively.
Emerging Trends in Sustainable Contracting:
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology has emerged as a promising tool for enhancing transparency and traceability in supply chains. By providing immutable records of transactions and product movements, blockchain can help organizations track and verify sustainability claims throughout the supply chain. Smart contract drafting executed on blockchain platforms can automate contract terms and conditions, including sustainability requirements, and facilitate real-time monitoring of compliance.
- Supplier Collaboration Platforms: Emerging supplier collaboration platforms enable closer collaboration between buyers and suppliers on sustainability initiatives. These platforms facilitate the sharing of data and best practices, enabling organizations to work together to address sustainability challenges and drive continuous improvement in supply chain sustainability performance.
- Carbon Offsetting Contracts: With an increasing focus on carbon emissions reduction, carbon offsetting contract drafting is gaining traction in sustainable contracting. These contracts involve agreements between buyers and suppliers to offset carbon emissions associated with products or services through investments in carbon offset projects, helping organizations achieve their sustainability goals.
Anticipated Regulatory Changes:
- Strengthened Reporting Requirements: Anticipated regulatory changes may include strengthened reporting requirements for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. These regulations would require organizations to disclose more detailed information about their sustainability practices and impacts, driving greater transparency and accountability in supply chain operations.
- Mandatory Due Diligence Legislation: Some jurisdictions are considering mandatory due diligence legislation that would require companies to identify, prevent, and mitigate human rights and environmental risks throughout their supply chains. These regulations would have significant implications for supply chain contracts, requiring organizations to conduct thorough risk assessments and implement robust due diligence processes to ensure compliance.
- Enhanced Enforcement Mechanisms: Regulatory changes may also include enhanced enforcement mechanisms and penalties for non-compliance with sustainability regulations. Organizations will need to proactively manage compliance risks and ensure that their supply chain contract drafting incorporates adequate provisions to address regulatory requirements and mitigate potential liabilities.
Conclusion
Incorporating environmental and social responsibility into supply chain contracts is crucial for building sustainable and resilient business practices. Contract drafting and management play a pivotal role in facilitating this integration, providing the framework for establishing and enforcing sustainability commitments throughout the supply chain. By embracing sustainable contracting practices, businesses can not only mitigate risks and enhance their reputation but also contribute to a more equitable and environmentally conscious global economy.
Blogs related to Contract Drafting:
Contract Drafting: ESG in Action: Weaving Sustainability Clauses
Digital Contract Drafting: Securely Streamlining M&A in the Cloud