In recent years, there has been a significant shift in the business landscape, with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations gaining prominence alongside financial performance. Companies are now being evaluated not only on their profitability but also on their impact on the environment, society, and governance practices. In response to this shift, integrating sustainability clauses into contract drafting has emerged as a powerful strategy for organizations to showcase their commitment to ESG principles. In this article, we delve into the importance of incorporating sustainability clauses into contracts and explore how contract drafting and contract management can be leveraged effectively to achieve this goal.
Understanding ESG and Its Relevance in Contracting
ESG, or Environmental, Social, and Governance, represents a multifaceted framework used to assess a company’s sustainability and societal impact. It encompasses a broad spectrum of factors that reflect the company’s commitment to responsible and ethical business practices. Environmental criteria within the ESG framework evaluate the company’s efforts to minimize its ecological footprint and mitigate environmental risks.
This may include initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions, conserving natural resources, and adopting sustainable practices in manufacturing and operations. Social criteria, on the other hand, focus on the company’s relationships with its various stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities.
This involves considerations such as fair labor practices, employee diversity and inclusion, customer satisfaction, and community engagement initiatives. Lastly, governance criteria assess the company’s corporate governance practices, transparency, and ethical standards. This includes factors such as the composition of the board of directors, executive compensation practices, adherence to legal and regulatory requirements, and the overall governance structure.
Together, these three pillars of ESG provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating a company’s overall sustainability performance and societal impact. Companies that excel across all three dimensions of ESG are often seen as more resilient, responsible, and attractive to investors and other stakeholders.
Sustainability Clauses: Explanation
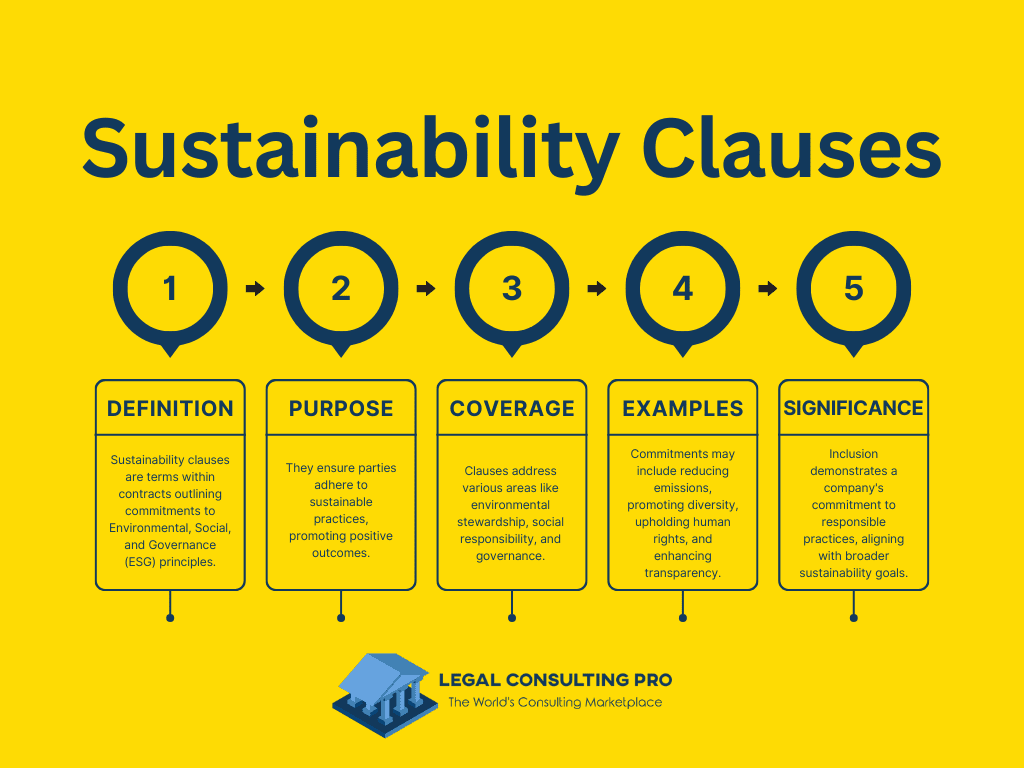
Sustainability clauses are provisions or terms embedded within contract drafting that outline specific commitments, requirements, or expectations related to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. These clauses are designed to ensure that parties to the contract adhere to sustainable business practices and contribute to positive environmental, social, and governance outcomes.
Sustainability clauses can cover a wide range of issues, including environmental stewardship, social responsibility, ethical business conduct, and corporate governance practices. Examples of sustainability clauses may include commitments to reduce carbon emissions, promote diversity and inclusion, uphold human rights standards, or enhance transparency and accountability in corporate governance.
The inclusion of sustainability clauses in contract drafting demonstrates a company’s commitment to responsible business practices and aligns with broader efforts to address sustainability challenges and achieve long-term societal and environmental goals.
Integrating Sustainability Clauses in Contract Drafting
Contract drafting represents the foundational cornerstone where sustainability clauses are seamlessly woven into legal agreements, shaping the trajectory of an organization’s commitment to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. These clauses serve as the bedrock, articulating with precision the specific actions and requirements expected from all involved parties.
For instance, a sustainability clause might mandate stringent environmental standards for suppliers, necessitating substantial reductions in carbon emissions or strict adherence to sustainable sourcing practices. Likewise, contractors may find themselves beholden to stringent mandates ensuring the maintenance of fair labor practices, guaranteeing equitable treatment for their workforce.
Moreover, contract drafting can be imbued with provisions explicitly designed for the monitoring and reporting of sustainability performance, thereby instilling a culture of unwavering accountability and transparency throughout the entirety of the contractual relationship. Through the meticulous implementation of these mechanisms, stakeholders are empowered to meticulously track progress, pinpoint areas ripe for improvement, and steadfastly uphold the organization’s sustainability objectives with resolute diligence and unwavering integrity.
Key Considerations in Contract Management
Effective contract management plays a pivotal role in upholding sustainability clauses throughout the contract lifecycle. After contracts are executed, meticulous oversight and enforcement are necessary to ensure that parties adhere to their commitments to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. Contract management encompasses a range of activities aimed at tracking obligations, monitoring performance, and enforcing compliance with sustainability requirements. This article explores the importance of contract management in ensuring the integrity of sustainability clauses and outlines key steps involved in managing contract drafting with sustainability provisions.
Elaboration in Points:
Tracking Contract Obligations:
- Contract management involves meticulously tracking the obligations outlined in the contract, including those related to sustainability.
- This entails identifying specific actions and requirements stipulated in the sustainability clauses and ensuring that all parties understand and fulfill their respective obligations.
Monitoring Performance:
- Effective contract management requires ongoing monitoring of performance to assess adherence to sustainability requirements.
- This may involve collecting data on key performance indicators (KPIs) related to ESG metrics, such as energy consumption, waste reduction, or diversity and inclusion initiatives.
- Regular performance evaluations allow stakeholders to identify areas of improvement and take corrective actions as needed.
Enforcing Compliance with Sustainability Requirements:
- Contract management also entails enforcing compliance with sustainability requirements outlined in the contract.
- This may involve implementing systems and processes to verify compliance, such as audits, inspections, or certifications.
- Enforcing compliance ensures that parties uphold their commitments to ESG principles and mitigates the risk of non-compliance or reputational damage.
Data Collection and Analysis:
- Contract management involves collecting and analyzing data related to ESG metrics to assess sustainability performance.
- This may include gathering information on environmental impact, social initiatives, or governance practices.
- Data analysis provides valuable insights into sustainability performance and informs decision-making processes.
Reporting and Auditing Sustainability Performance:
- Contract management includes establishing mechanisms for reporting and auditing sustainability performance.
- This may involve preparing regular reports on ESG performance for stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and the public.
- Auditing sustainability performance ensures transparency and accountability and demonstrates the organization’s commitment to sustainable business practices.
In summary, effective contract management is essential for upholding sustainability clauses throughout the contract lifecycle. By tracking obligations, monitoring performance, and enforcing compliance with sustainability requirements, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to ESG principles and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Benefits of Incorporating Sustainability Clauses
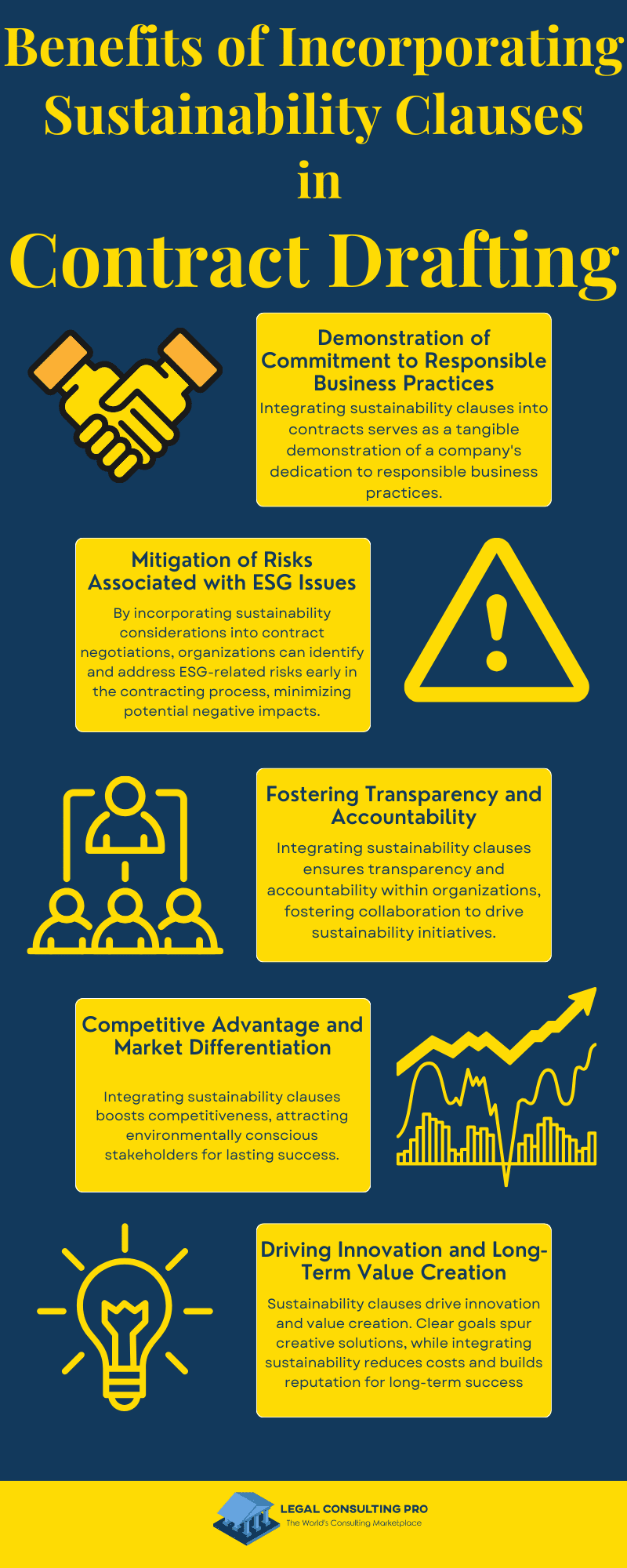
Demonstration of Commitment to Responsible Business Practices:
- Integrating sustainability clauses into contracts serves as a tangible demonstration of a company’s dedication to responsible business practices.
- This proactive approach signals to stakeholders, including customers, investors, and employees, that the organization prioritizes sustainability and ethical considerations.
- By publicly committing to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles through contractual agreements, the company enhances its reputation and brand value, positioning itself as a leader in sustainable business practices.
Mitigation of Risks Associated with ESG Issues:
- Sustainability clauses in contract drafting help organizations mitigate risks associated with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues.
- Explicitly outlining sustainability requirements and expectations enables organizations to proactively address potential risks, such as regulatory non-compliance or reputational damage.
- Compliance with sustainability clauses reduces the likelihood of legal and financial penalties resulting from violations of environmental regulations or breaches of social responsibilities.
- By incorporating sustainability considerations into contract negotiations, organizations can identify and address ESG-related risks early in the contracting process, minimizing potential negative impacts on the business.
Fostering Transparency and Accountability:
- Integrating sustainability clauses fosters transparency and accountability within organizations.
- Clear expectations for sustainable business practices set by sustainability clauses ensure that stakeholders are informed about the organization’s ESG commitments and performance.
- Regular reporting and monitoring of sustainability metrics, as required by sustainability clauses, promote transparency by providing stakeholders with visibility into the organization’s progress toward ESG goals.
- Accountability is reinforced as organizations are held responsible for fulfilling their commitments to sustainability, building trust and credibility with stakeholders.
- Fostering transparency and accountability encourages collaboration among stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, employees, and communities, in driving sustainability initiatives and achieving shared objectives.
Competitive Advantage and Market Differentiation:
- Integrating sustainability clauses into contract drafting can provide organizations with a competitive advantage and differentiate them in the market.
- Increasingly, consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies are prioritizing sustainability and ESG considerations when evaluating companies.
- Organizations that demonstrate a strong commitment to sustainability through contractual agreements may attract environmentally and socially conscious customers, investors, and partners.
- Furthermore, organizations with robust sustainability practices may be better positioned to access capital, secure partnerships, and attract top talent, enhancing their competitiveness and long-term success.
Driving Innovation and Long-Term Value Creation:
- Sustainability clauses in contract drafting can drive innovation and foster long-term value creation for organizations.
- By setting clear sustainability goals and expectations, organizations incentivize innovation and creativity in finding sustainable solutions to business challenges.
- Integrating sustainability considerations into contract negotiations encourages the adoption of environmentally friendly practices, resource efficiency, and social responsibility initiatives.
- Investing in sustainability not only benefits the environment and society but also contributes to long-term value creation for organizations by reducing costs, enhancing resilience, and building reputation and brand loyalty.
Challenges and Best Practices
Ensuring Enforceability and Clarity of Sustainability Provisions:
- One of the primary challenges in incorporating sustainability clauses into contract drafting is ensuring their enforceability and clarity.
- Sustainability clauses should be drafted with precision to avoid ambiguity and ensure that parties understand their obligations.
- Clauses should clearly define sustainability goals, metrics, and performance indicators to facilitate monitoring and enforcement.
Drafting SMART Clauses:
- To address the challenge of enforceability and clarity, legal professionals should draft sustainability clauses that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Specific clauses clearly articulate the desired sustainability outcomes and actions required from the parties.
- Measurable clauses include quantifiable metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess progress and compliance.
- Achievable clauses set realistic goals that parties can feasibly accomplish within the contract term.
- Relevant clauses align with the organization’s broader sustainability objectives and priorities.
- Time-bound clauses establish clear deadlines or milestones for achieving sustainability targets, ensuring accountability and progress tracking.
Collaboration Across Teams:
- Effective collaboration between legal, procurement, and sustainability teams is essential to align sustainability objectives with contractual requirements.
- Legal professionals work closely with sustainability and procurement teams to ensure that sustainability clauses are integrated seamlessly into contract drafting.
- Collaboration ensures that sustainability objectives are aligned with business goals and that contractual obligations support the organization’s broader sustainability strategy.
Integration of Sustainability into Contract Negotiations:
- Another challenge is integrating sustainability considerations into contract negotiations, particularly in complex contractual relationships.
- Legal professionals must advocate for the inclusion of sustainability clauses during negotiations and ensure that parties understand the importance of these provisions.
- Negotiating sustainability clauses may require compromise and flexibility to address the interests and concerns of all parties involved.
Monitoring and Enforcement Mechanisms:
- Establishing effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms is crucial for ensuring compliance with sustainability provisions.
- Contract drafting should include provisions for regular reporting, performance monitoring, and dispute resolution related to sustainability matters.
- Legal professionals collaborate with relevant stakeholders to develop monitoring protocols and mechanisms for addressing non-compliance effectively.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation:
- Finally, organizations must continuously review and adapt their sustainability clauses to evolving regulatory requirements, industry standards, and stakeholder expectations.
- Legal professionals play a key role in monitoring changes in sustainability laws and regulations and updating contract clauses accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness.
Conclusion: Embracing ESG Through Contracting
In conclusion, integrating sustainability clauses into contract drafting represents a proactive approach for organizations to embed Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles into their business operations. By incorporating sustainability considerations into contract drafting and management processes, companies can demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices, mitigate risks, and build trust with stakeholders. As the importance of ESG continues to grow, leveraging contract drafting and contract management to weave sustainability clauses into contracts will become increasingly vital for organizations seeking to thrive in a rapidly evolving business landscape. This strategic approach not only aligns with evolving stakeholder expectations but also positions companies to drive positive social and environmental impact while achieving long-term business success.
Similar blogs:
Digital Contract Drafting: Securely Streamlining M&A in the Cloud
NDA Contract Drafting in the Age of Open Innovation: What Startups Need to Know