Surveillance has become a common practice in workers’ compensation cases, used by Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts to gather evidence related to the extent of an injured worker’s disability or their activities outside of work. While surveillance can sometimes provide valuable information for assessing claims, its use raises important ethical considerations. This article explores the role of surveillance in workers’ compensation cases and examines the ethical implications associated with its use.
Understanding Legal Consulting Surveillance in Workers’ Compensation Cases
Surveillance in workers’ compensation cases encompasses a range of techniques utilized by Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts to gather information about an injured worker’s activities and behaviors. These techniques may include video recording, photography, or monitoring of social media channels. The primary Legal consulting objectives of surveillance are to validate the accuracy of reported injuries, evaluate the extent of disability, and identify any potential instances of fraud or exaggeration by the injured worker.
Video Recording:
- Video surveillance involves the discreet filming of an injured worker’s activities in various settings, such as at home, in public places, or while performing daily tasks.
- Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts may use video footage to observe the injured worker’s mobility, physical capabilities, and adherence to medical restrictions or limitations.
Photography:
- Photography surveillance entails capturing still images of the injured worker engaged in different activities or situations.
- Photographs may provide visual evidence of the injured worker’s activities, such as participation in recreational or social events, performing physical tasks, or engaging in activities inconsistent with reported injuries.
Social Media Monitoring:
- Social media surveillance involves monitoring the injured worker’s online activities and interactions on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter.
- Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts may analyze social media posts, photos, and comments to gather information about the injured worker’s lifestyle, activities, and behaviors that could potentially contradict reported injuries or limitations.
Verification of Reported Injuries:
- Surveillance is often used to verify the accuracy and validity of reported injuries by observing the injured worker’s activities and behaviors over time.
- Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts may compare the observed activities with the reported symptoms, limitations, or medical restrictions to assess the consistency of the injured worker’s claims.
Assessment of Disability Severity:
- Surveillance helps assess the severity of disability by documenting the injured worker’s functional abilities, mobility, and physical activities in different contexts.
- Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts may use surveillance findings to evaluate the extent of impairment and determine the injured worker’s eligibility for benefits or return-to-work readiness.
Detection of Fraud or Exaggeration:
- Surveillance is employed as a tool to detect potential instances of fraud or exaggeration by the injured worker, such as claiming disability benefits while engaging in activities inconsistent with reported injuries.
- Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts scrutinize surveillance footage or photographs to identify discrepancies between the injured worker’s reported limitations and their observed behaviors or activities.
In summary, surveillance in workers’ compensation cases serves as a mechanism for Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts to gather objective evidence regarding an injured worker’s activities, behaviors, and functional abilities. While aimed at verifying the accuracy of reported injuries and preventing fraud, the use of surveillance techniques must be conducted within legal consulting and ethical boundaries, respecting the privacy and rights of the injured worker.
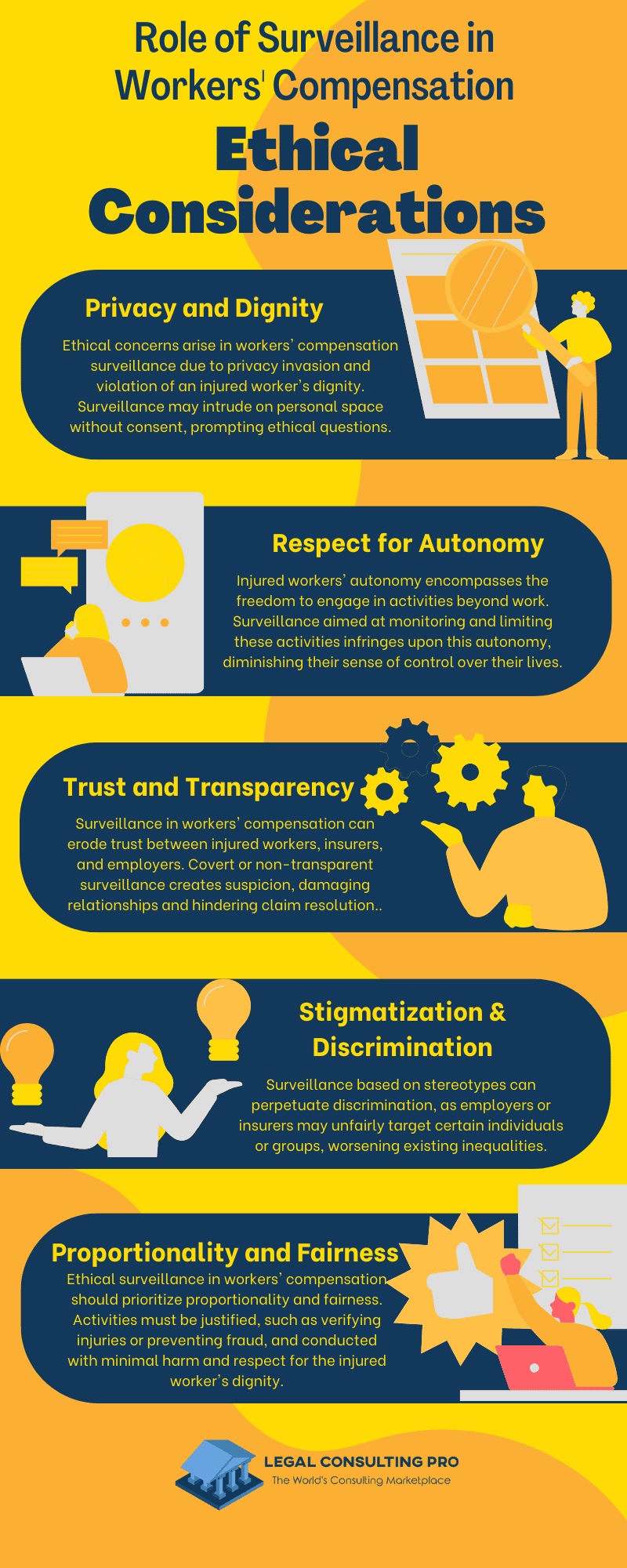
Ethical Considerations
Privacy and Dignity
One of the primary ethical concerns surrounding surveillance in workers’ compensation cases is the invasion of privacy and the violation of an injured worker’s dignity. Surveillance activities, which may include covert video recording or monitoring of social media, have the potential to intrude into an individual’s personal space and capture private moments without their consent. Such practices raise significant ethical questions about the appropriateness and ethicality of surveillance tactics.
Injured workers have a reasonable expectation of privacy, and the clandestine nature of surveillance may undermine their sense of autonomy and dignity. The lack of transparency and consent further exacerbates these ethical concerns, as individuals may be unaware that they are under surveillance or have not consented to such monitoring.
Moreover, the risk of stigmatization and psychological harm due to the perceived intrusion into their private lives compounds the ethical dilemmas associated with surveillance in workers’ compensation cases. Ultimately, navigating these ethical complexities requires a careful balance between the legitimate interests of Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts and the protection of the fundamental rights and dignity of injured workers.
Respect for Autonomy
Injured workers possess fundamental rights to autonomy and self-determination, encompassing the freedom to engage in activities of their choosing beyond the realm of work. Surveillance practices aimed at monitoring and constraining an individual’s activities have the potential to infringe upon these rights, resulting in a violation of their autonomy and impeding their ability to exercise control over their own lives.
By subjecting injured workers to constant scrutiny and surveillance, such practices undermine their sense of agency and diminish their capacity to make decisions in alignment with their personal preferences and values. Furthermore, surveillance that seeks to monitor and restrict an individual’s activities may create an environment of distrust and suspicion, eroding the mutual respect and cooperation essential for fostering positive relationships between employers and employees.
Upholding the rights of injured workers to autonomy and self-determination necessitates a respectful and balanced approach to surveillance, one that prioritizes transparency, consent, and respect for individual freedoms while addressing legitimate concerns related to workers’ compensation claims and workplace safety.
Trust and Transparency
Surveillance in workers’ compensation cases can potentially deteriorate trust among key stakeholders, including injured workers, insurers, and employers. When surveillance activities are carried out covertly or without transparency, it fosters an atmosphere of suspicion and animosity, leading to a breakdown in trust and hindering the resolution of claims.
Injured workers may feel that their privacy is being violated and that their integrity is being questioned, which can evoke feelings of resentment and hostility towards Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts. Similarly, Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts may perceive injured workers as untrustworthy or deceptive, further exacerbating tensions and impeding cooperation in the claims process.
As trust erodes, communication becomes strained, and the likelihood of reaching mutually agreeable resolutions diminishes. Moreover, the adversarial dynamic created by covert surveillance can escalate disputes and prolong the claims process, ultimately undermining the well-being of injured workers and delaying their access to necessary benefits and support.
To foster a collaborative and constructive environment for resolving workers’ compensation claims, it is essential to prioritize transparency, respect for privacy rights, and open communication among all stakeholders involved. By fostering trust and cooperation, transparent surveillance practices can contribute to more efficient and equitable outcomes in workers’ compensation cases, benefiting both injured workers and the broader workforce.
Stigmatization and Discrimination
Surveillance in workers’ compensation, influenced by stereotypes, has the potential to deepen stigmatization and discrimination within the workplace. When certain individuals or demographic groups are singled out for scrutiny based on biased assumptions, it not only results in unfair treatment but also perpetuates systemic inequalities.
To counter this, employers and insurers need to adopt surveillance practices that are transparent, impartial, and based on legitimate grounds rather than preconceived notions.
Moreover, fostering a culture of diversity and inclusion is crucial for challenging discriminatory beliefs and creating a workplace environment where all employees, regardless of their health status or background, are treated with respect and dignity. By promoting fairness and equity in surveillance and workplace policies, organizations can work towards creating a more supportive and inclusive work environment for everyone.
Proportionality and Fairness
Ethical surveillance practices in workers’ compensation cases should be anchored in the principles of proportionality and fairness. It is imperative that surveillance activities are justified by legitimate reasons, such as ensuring the accuracy of reported injuries or preventing fraud, and are conducted with sensitivity towards the dignity of the injured worker.
Employers and insurers must carefully assess the necessity of surveillance, opting for measures proportionate to the objectives being pursued and minimizing harm to the individual under surveillance. This entails avoiding excessive or indiscriminate surveillance tactics that may infringe upon the privacy and rights of the injured worker.
Moreover, ethical surveillance practices prioritize transparency and accountability, with clear communication about the reasons for surveillance and robust oversight mechanisms to ensure adherence to ethical principles and legal consulting requirements. By upholding these standards, employers and insurers can maintain the integrity of surveillance practices while respecting the rights and dignity of injured workers, fostering trust and fairness within the workers’ compensation system.
Best Practices for Ethical Surveillance:
- Transparency: Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts should be transparent about the use of surveillance in workers’ compensation cases, informing injured workers of the possibility of surveillance and the reasons for its use.
- Procedural Safeguards: There should be clear procedures in place for the collection, storage, and use of surveillance evidence, including mechanisms for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information obtained.
- Respect for Privacy: Surveillance activities should respect the privacy and dignity of injured workers, avoiding invasive or intrusive methods that violate their personal space or capture sensitive information.
- Accountability: Insurers, employers, and legal consulting experts should be accountable for their surveillance practices, subject to oversight and review by regulatory authorities or independent bodies to ensure compliance with ethical standards and legal consulting requirements.
- Fairness and Non-Discrimination: Surveillance should be conducted in a manner that is fair, impartial, and free from discrimination, avoiding the targeting of specific individuals or groups based on stereotypes or biases.
Conclusion
Surveillance plays a contentious role in workers’ compensation cases, with ethical considerations surrounding privacy, autonomy, trust, and fairness. While surveillance can serve legitimate purposes, its use must be guided by ethical principles that prioritize respect for the rights and dignity of injured workers. By adhering to transparency, procedural safeguards, and accountability mechanisms, stakeholders can ensure that surveillance practices in workers’ compensation cases are conducted ethically and responsibly.
Similar blogs:
A Legal Consulting Perspective For The Role of Vocational Rehabilitation in Workers’ Compensation
Legal Consulting: Mental Health and Workers’ Compensation: Addressing PTSD and Stress Claims