In the realm of workers’ compensation, the focus has traditionally been on physical injuries sustained in the workplace. However, the recognition of mental health issues, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and stress-related claims, is gaining prominence. This shift reflects a broader acknowledgment of the impact of work-related stressors on an individual’s mental well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intersection of mental health and workers’ compensation, delving into the challenges, legal consulting considerations, and strategies for addressing PTSD and stress claims.
Understanding Mental Health in the Workplace
Changing Dynamics
The landscape of workers’ compensation is evolving to encompass mental health concerns, reflecting a growing recognition of the importance of mental well-being in the workplace. Employers and organizations are adapting to this shift, acknowledging that mental health is a vital component of overall employee welfare. This changing dynamic signals a departure from traditional views, paving the way for a more comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and mental health aspects in the workplace.
Common Mental Health Challenges in the Workplace
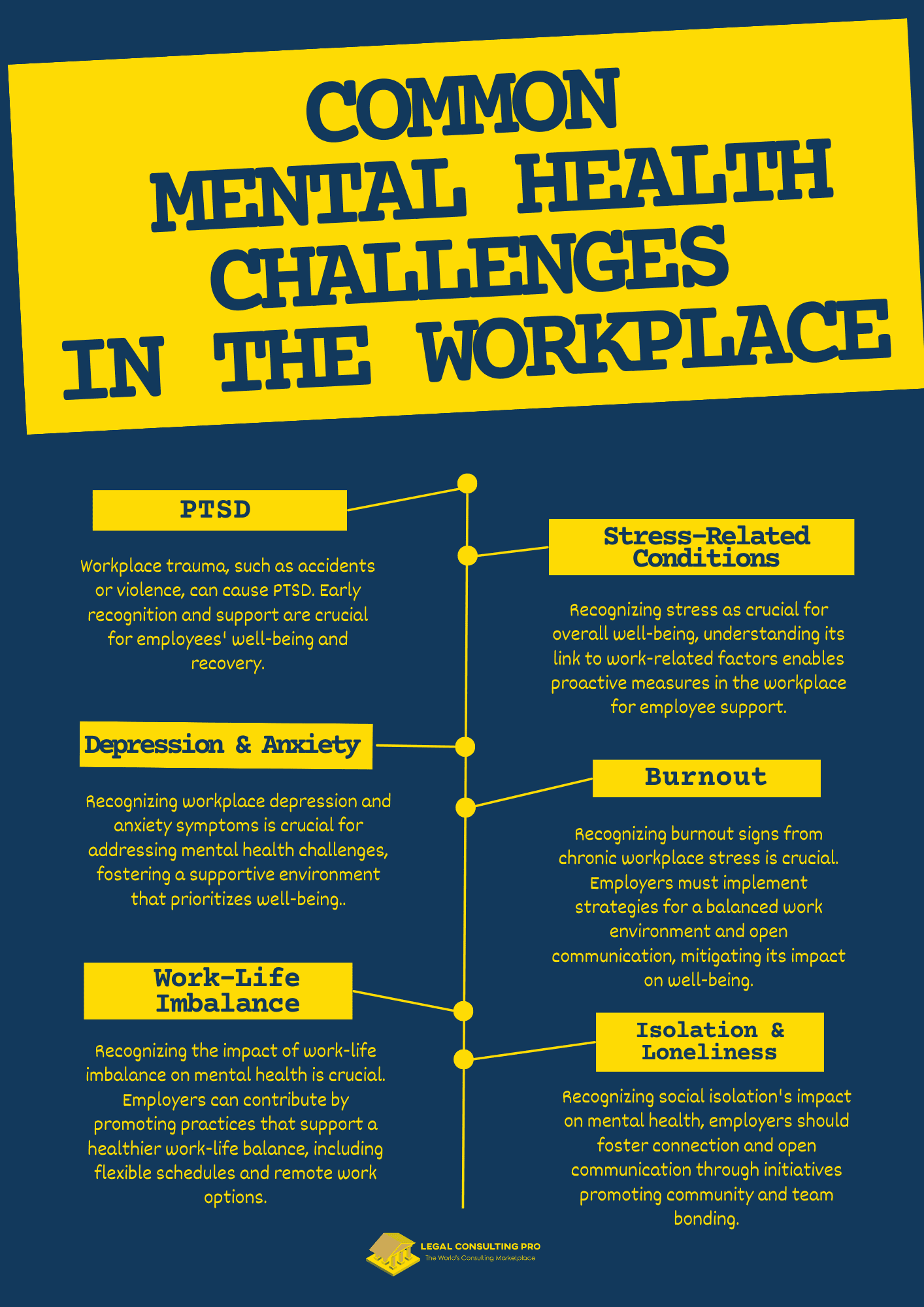
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition arising from exposure to traumatic events. Recognizing the profound impact of such experiences is crucial. In the workplace, trauma, whether from accidents, violence, or critical incidents, can lead to PTSD, affecting employees’ mental and emotional well-being. Early recognition and supportive measures are essential for recovery.
Stress-Related Conditions:
Stress-related conditions encompass mental health challenges arising from prolonged stress. Recognizing stress as a pervasive issue is vital for overall well-being. In the workplace, understanding the correlation between stressors like high workload and mental health issues enables proactive measures, fostering supportive environments to mitigate the adverse effects of stress on employees’ mental well-being.
Depression and Anxiety:
Recognizing symptoms of depression and anxiety in the workplace is essential for addressing mental health challenges. Raising awareness about the prevalence of these conditions helps reduce stigma, fostering an open and supportive environment. By encouraging understanding and empathy, workplaces contribute to a culture that prioritizes mental well-being and inclusivity.
Burnout:
Recognizing signs of burnout, linked to chronic workplace stress, is crucial. Employers must implement preventative strategies and support mechanisms to address employee burnout. This involves fostering a balanced work environment, encouraging self-care practices, and promoting open communication to mitigate the impact of prolonged stress on individuals’ well-being.
Work-Life Imbalance:
Acknowledging the impact of work-life imbalance on mental health is vital. Striking a balance between professional and personal life is crucial for overall well-being. Employers can contribute by promoting practices that support a healthier work-life balance, such as flexible schedules, remote work options, and initiatives that prioritize employee mental and emotional health.
Isolation and Loneliness:
Recognizing the adverse effects of social isolation and loneliness on mental well-being is imperative. Employers should actively encourage and cultivate a workplace culture that prioritizes connection, collaboration, and open communication. Initiatives fostering a sense of community, team bonding activities, and supportive networks can contribute to mitigating the negative impact of isolation on employees’ mental health.
Legal consulting Considerations
- Recognition of Mental Health Claims: The legal consulting evolution recognizing mental health in workers’ compensation claims signifies a paradigm shift. Landmark cases and legislative changes have catalyzed this recognition, emphasizing the legal consulting obligation to address mental health issues on par with physical ailments. This acknowledgment reflects a broader societal understanding of the complex interplay between work conditions and mental well-being, promoting fairness and inclusivity in compensation frameworks.
- Criteria for PTSD Claims: Establishing PTSD claims within the legal consulting framework involves navigating specific criteria. Legal considerations include examining the direct link between work-related incidents and PTSD development. Challenges lie in demonstrating the causation between work factors and mental health outcomes. Legal discussions often delve into the nuanced nature of traumatic events, emphasizing the need for a thorough assessment of the workplace’s role in triggering and exacerbating PTSD.
- Stress-Related Claims: Legal considerations for stress-related claims encompass a spectrum of mental health conditions arising from workplace stressors. This includes work-induced anxiety and depression. The legal consulting landscape outlines criteria for proving the connection between workplace conditions and mental health issues. Discussions revolve around defining the burden of proof, requiring comprehensive evidence to substantiate stress-related claims. Legal consulting frameworks aim to strike a balance between acknowledging genuine concerns and preventing abuse of the system.
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations: Legal consulting considerations extend to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) regulations, which play a vital role in safeguarding employee well-being. Employers are legally obligated to provide a safe and healthy work environment. Breaches of OHS regulations may result in legal consulting consequences, emphasizing the need for organizations to proactively address workplace stressors and mental health concerns to comply with legal standards.
- Anti-Discrimination Laws: Legal safeguards against discrimination based on mental health are critical considerations. Anti-discrimination laws protect employees from adverse actions based on their mental health status. Employers are legally bound to create a workplace free from discrimination, fostering an environment that supports employees with mental health conditions and ensuring legal consulting consequences for discriminatory practices.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Navigating privacy and confidentiality is paramount in mental health legal considerations. Laws safeguarding employee privacy rights must be upheld, requiring employers to handle mental health information confidentially. Legal consulting frameworks ensure that employees feel secure in seeking assistance without fear of privacy breaches, fostering an environment conducive to open dialogue about mental health challenges.
- Reasonable Accommodations: Legal obligations extend to providing reasonable accommodations for employees with mental health conditions. Employers must navigate these legal considerations by making adjustments to work environments or duties that facilitate employees’ continued productivity while addressing their mental health needs. This legal aspect emphasizes inclusivity and equal opportunities for employees managing mental health challenges.
Challenges and Stigmas
Overcoming Stigmas
- Addressing Societal Stigmas: Confronting societal stigmas surrounding mental health in the workplace is a significant challenge. This involves fostering a culture that promotes open discussions, reduces stigma, and encourages employees to seek help without fear of judgment.
- Challenges in Seeking Compensation: Employees face hurdles in seeking compensation for mental health-related injuries due to lingering stigmas. Overcoming these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving awareness campaigns, education, and changes in organizational culture to create an environment where mental health issues are treated with the same seriousness as physical injuries.
Subjectivity of Mental Health Claims
- Exploring Inherent Subjectivity: Mental health diagnoses inherently involve subjectivity, posing a challenge in workers’ compensation claims. The interpretation of symptoms, severity, and the impact on work capacity can vary. Recognizing this subjectivity is crucial in understanding the unique nature of mental health conditions and their implications for compensation.
- Navigating Subjectivity in Legal Consulting Systems: Legal systems must navigate the subjective nature of mental health conditions when assessing workers’ compensation claims. This involves developing frameworks that consider expert opinions, medical evidence, and the individualized nature of mental health experiences. Striking a balance between objective criteria and acknowledging subjectivity is vital for fair and equitable treatment in legal processes.
Strategies for Employers and Employees:
Workplace Policies and Prevention:
Proactive Measures to Prevent Stressors:
- Conduct regular stress assessments to identify potential triggers.
- Address workload issues and promote a healthy work-life balance.
- Foster a culture that values open communication and provides outlets for stress relief.
Comprehensive Workplace Policies:
- Develop clear policies addressing mental health concerns.
- Destigmatize mental health discussions within the workplace.
- Promote inclusivity and diversity to create an accepting work environment.
Early Intervention and Support Programs:
Benefits of Early Intervention:
- Offer Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) providing counseling and support.
- Facilitate training for managers to recognize early signs of mental health challenges.
- Implement a culture of regular check-ins to monitor employee well-being.
Mitigating Likelihood of Workers’ Compensation Claims:
- Provide resources for stress management and mental health education.
- Establish confidential reporting channels for employees to seek help.
- Collaborate with mental health professionals to offer specialized support.
Promoting Mental Health Awareness:
Educational Initiatives:
- Conduct regular mental health awareness training for employees and managers.
- Promote understanding of mental health through workshops and seminars.
- Share resources and information about available mental health support.
Employee Resource Groups:
- Create employee resource groups focused on mental health.
- Encourage peer support and mentorship within these groups.
- Use these groups as platforms for open discussions and sharing experiences.
These strategies collectively contribute to a workplace culture that prioritizes mental health, encourages open communication, and fosters a supportive environment for all employees.
Conclusion
As the landscape of workers’ compensation expands to encompass mental health considerations, employers, employees, and legal consulting professionals must navigate this complex terrain with understanding and empathy. By addressing PTSD and stress claims comprehensively, we can foster workplaces that prioritize mental well-being and provide support for those facing mental health challenges. This guide serves as a roadmap for stakeholders seeking to navigate the evolving intersection of mental health and workers’ compensation.
Similar blogs:
Navigating Permanent Disability: Legal Consulting Guide For Workers’ Compensation Lawyers
Secret Weapon Unveiled: How Medical Evidence Wins Big in Workers’ Compensation Cases