In today’s data-driven world, cybersecurity is paramount for protecting sensitive information and maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders. As businesses increasingly rely on digital technologies to store and process data, the need for robust cybersecurity measures and contractual safeguards has never been greater. In this article, we’ll explore a comprehensive cybersecurity contract drafting checklist, outlining essential clauses that every data-driven business should consider to mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
Clear Definition of Terms: Cybersecurity Contracts
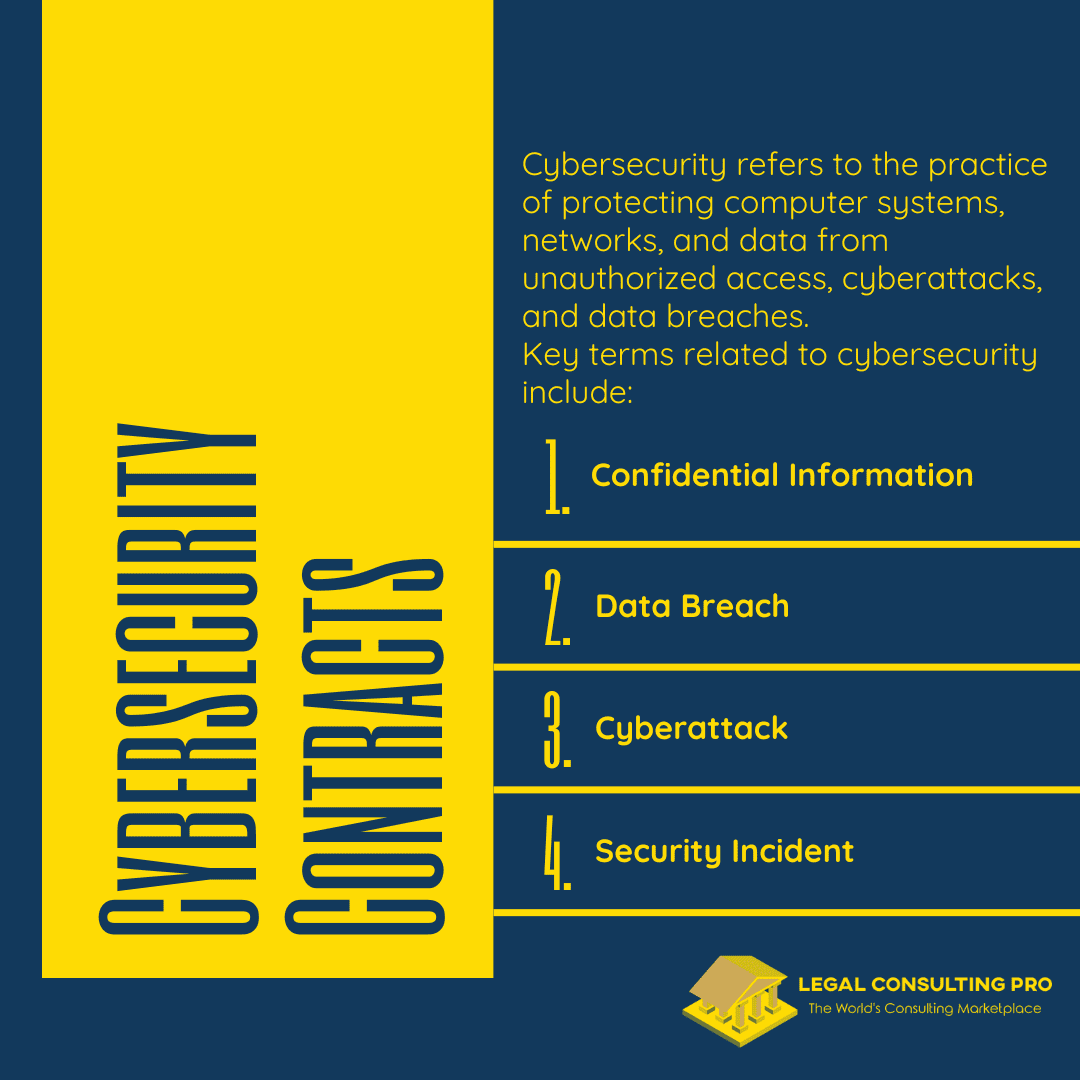
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. It encompasses various technologies, processes, and practices designed to safeguard digital assets and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
Key terms related to cybersecurity include:
- Confidential Information: Sensitive data that requires protection from unauthorized disclosure or access, such as personal identifiable information (PII), trade secrets, and proprietary business information.
- Data Breach: An incident where unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive or confidential data without authorization, potentially resulting in its disclosure, theft, or compromise.
- Cyberattack: Deliberate actions carried out by malicious actors or hackers to exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems or networks, with the intent to disrupt operations, steal data, or cause damage.
- Security Incident: Any event that compromises or threatens the security of computer systems, networks, or data, including unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and denial-of-service attacks.
By clearly defining these terms upfront in a contract, parties can ensure a common understanding of cybersecurity-related concepts and requirements, facilitating effective communication, collaboration, and risk management efforts. This clarity helps mitigate the potential for misunderstandings or disputes and promotes consistency in addressing cybersecurity concerns throughout the contract drafting lifecycle.
Importance of Data Protection and Privacy in Cybersecurity Contract Drafting
In the context of cybersecurity contract drafting, it’s crucial to address data protection and privacy concerns comprehensively. This entails including clauses that outline the obligations of each party regarding the safeguarding of sensitive information and adherence to applicable data protection regulations. For instance, if the business operates in the European Union, compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is paramount, while businesses in California must adhere to the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Additionally, entities handling healthcare data must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
These clauses should specify the measures that each party will take to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse. This may include implementing robust cybersecurity measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments. Furthermore, it’s essential to outline data retention and deletion policies, specifying how long data will be retained and the procedures for securely disposing of it once it’s no longer needed. This helps mitigate the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access by ensuring that data is only retained for as long as necessary and is securely disposed of when no longer needed.
By addressing data protection and privacy concerns in the contract drafting, parties can demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding sensitive information and complying with applicable regulations, fostering trust and confidence among stakeholders.
Security Measures and Standards: Cybersecurity Contracts
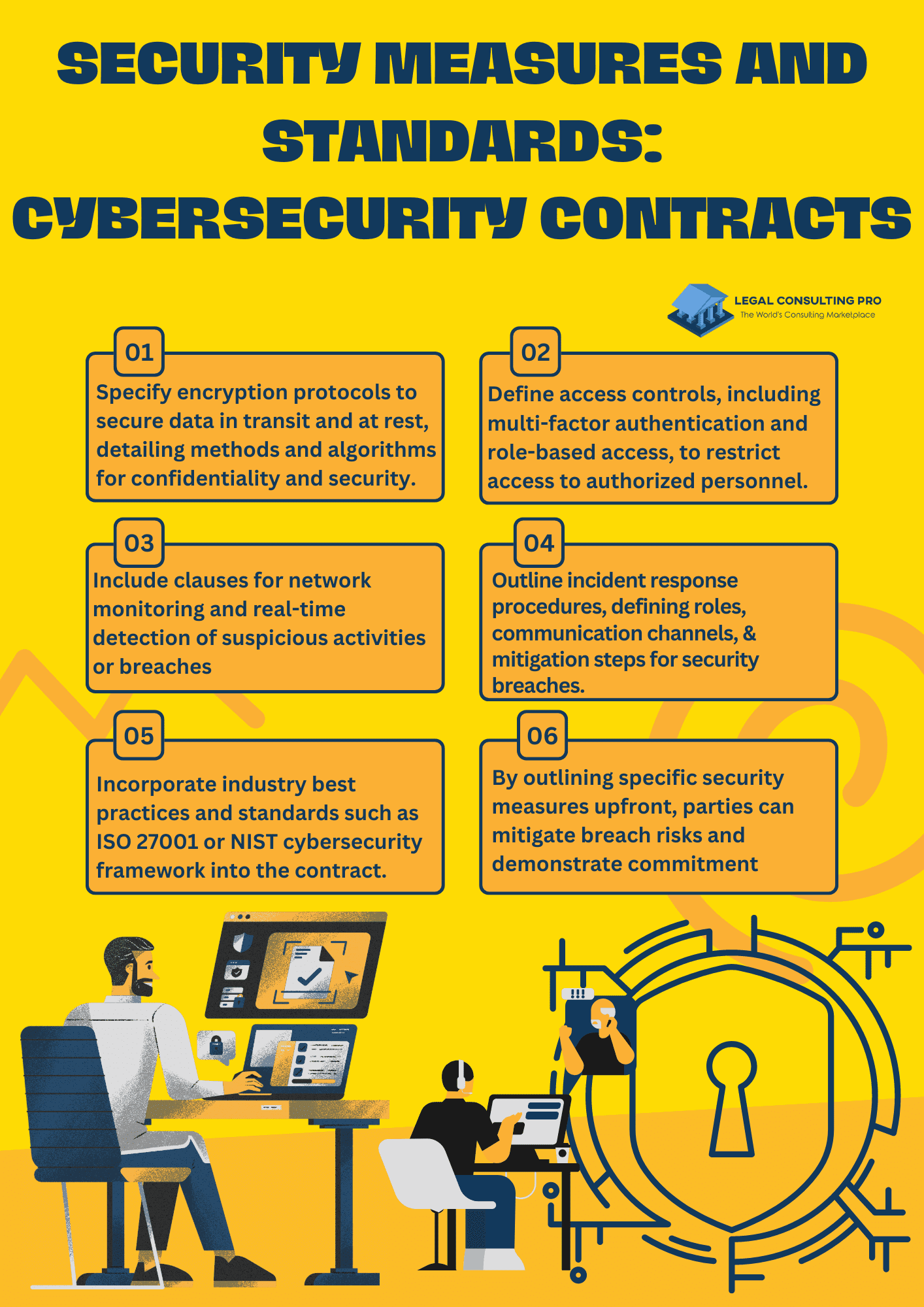
In the realm of cybersecurity contract drafting, outlining specific security measures and standards is paramount to ensuring a robust defense against cyber threats. These clauses should delineate the security protocols and practices that both parties are obligated to adhere to throughout the duration of the contract.
First and foremost, encryption protocols should be clearly specified, outlining the encryption methods and algorithms to be used for protecting sensitive data both in transit and at rest. This ensures that data remains confidential and secure, even if intercepted by unauthorized parties.
Access controls are another crucial aspect to address, defining the mechanisms for granting and revoking access to systems and data. This involves implementing user authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls to limit access to authorized personnel only.
Network monitoring clauses should also be included to ensure proactive detection of suspicious activities or security breaches. This involves deploying monitoring tools and technologies to continuously monitor network traffic and system logs for signs of unauthorized access or malicious behavior.
Additionally, incident response procedures should be clearly outlined to ensure a prompt and coordinated response in the event of a security incident or breach. This includes defining the roles and responsibilities of each party during an incident, establishing communication channels for reporting incidents, and outlining the steps to be taken to mitigate the impact of the incident and restore normal operations.
Incorporating industry best practices and standards, such as the ISO 27001 or NIST cybersecurity framework, into the contract drafting provides a clear framework for security implementation and assessment. This ensures that both parties are aligned with recognized industry standards and are committed to maintaining a high level of security throughout the duration of the contract.
By specifying these security measures and standards upfront, parties can mitigate the risk of security breaches and demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding sensitive data and assets.
Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure
By including robust confidentiality and non-disclosure clauses in the contract, parties can protect sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure or use, safeguarding their proprietary interests and preserving the confidentiality of valuable business assets.
Additionally, addressing the handling of confidential information upon termination or expiration of the contract management ensures that data remains protected even after the business relationship has ended, providing peace of mind to both parties involved.
Confidentiality and Non-disclosure Clauses:
- Define the scope of confidential information: Clearly outline the types of information considered confidential, including proprietary business data, trade secrets, and any other sensitive information exchanged between the parties.
- Specify obligations: Clearly delineate the responsibilities of each party in safeguarding confidential information from unauthorized disclosure or use. This may include implementing appropriate security measures, restricting access to authorized personnel only, and prohibiting the sharing of confidential information with third parties without prior consent.
- Include exceptions: Consider including exceptions to the confidentiality obligations, such as information that is already in the public domain or information that becomes known to the receiving party through legitimate means other than the disclosing party.
Handling of Confidential Information upon Termination or Expiration:
- Continuation of obligations: Clearly state that the obligations regarding the handling of confidential information will survive the termination or expiration of the contract. This ensures that parties remain bound by their confidentiality obligations even after the business relationship has ended.
- Return or destruction of information: Specify the procedures for the return or destruction of confidential information upon termination or expiration of the contract. This may involve requiring the receiving party to promptly return or destroy all confidential information and certify in writing that it has done so.
- Extended confidentiality: Consider including provisions for extended confidentiality obligations for certain types of information, such as trade secrets, which may continue to be protected even after the contract management has ended.
Third-Party Service Providers
In any contract management involving cybersecurity and data management, it’s essential to address the involvement of third-party service providers. These providers often play a crucial role in implementing security measures and managing data on behalf of the contracting parties. Therefore, it’s important to include clauses that clearly outline the requirements and responsibilities of these third-party vendors. This includes defining the scope of services they will provide, specifying their obligations regarding data protection and security, and outlining the standards they must adhere to.
Additionally, the contract management should establish mechanisms for monitoring and auditing the performance of third-party providers to ensure ongoing compliance. By incorporating these clauses, organizations can effectively manage the risks associated with third-party dependencies and maintain the integrity and security of their data assets.
Data Breach Response and Notification
In contract drafting involving cybersecurity, it’s imperative to establish clear procedures for responding to data breaches or cyber security incidents. This includes defining the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, such as notification requirements, escalation protocols, and responsibilities for investigation and remediation. By outlining these procedures upfront, parties can ensure a swift and coordinated response to any security incidents, minimizing the impact on data integrity and stakeholder trust.
Additionally, the contract management should define the timeline and criteria for notifying affected parties, regulatory authorities, and other stakeholders in the event of a data breach. This helps ensure compliance with legal obligations and allows for timely mitigation measures to be implemented, reducing potential harm to individuals or the business.
Indemnification and Liability
In cybersecurity contract drafting, it’s crucial to address indemnification and liability provisions to allocate responsibility for losses or damages arising from breaches or non-compliance. This involves specifying the scope of indemnification, including any limitations or exclusions, to ensure clarity and fairness in distributing liabilities between parties.
Additionally, outlining the process for resolving disputes related to cybersecurity incidents or breaches helps streamline the resolution process and mitigate potential legal conflicts. By clearly defining indemnification and liability terms, parties can proactively manage risks associated with cybersecurity breaches and uphold accountability in contract drafting agreements.
Compliance Monitoring and Auditing
In cybersecurity contract drafting, incorporating clauses for regular compliance monitoring and auditing is essential for assessing security effectiveness, identifying vulnerabilities, and ensuring ongoing compliance with contractual and regulatory obligations. These clauses define the frequency, scope, and methods of auditing, outlining responsibilities for facilitating and cooperating with audits.
By establishing clear monitoring and auditing procedures, parties can proactively assess their security posture, address potential risks, and demonstrate adherence to contractual and regulatory standards. This proactive approach helps bolster trust and confidence among stakeholders and enhances overall cybersecurity resilience.
Conclusion
A robust cybersecurity contract drafting checklist is essential for every data-driven business to protect sensitive information, mitigate risks, and maintain regulatory compliance. By including essential clauses addressing data protection, security measures, confidentiality, third-party engagements, breach response, indemnification, and compliance monitoring, businesses can establish a solid foundation for cybersecurity in their contractual relationships.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it is crucial for businesses to regularly review and update their contracts to address emerging risks and vulnerabilities effectively.
Similar Blogs:
The Rise of Virtual Contract Drafting: From Zoom to Metaverse: Adapting Contract Language
The Future of LegalTech: How to Leverage Technology for Faster Contract Drafting