The landscape of contract drafting and negotiation has undergone a profound transformation in recent years, driven by the widespread adoption of virtual communication tools and the emergence of immersive technologies like the Metaverse. This article delves into the evolving realm of virtual contract management and drafting, exploring how legal professionals can adapt contract drafting language to meet the challenges and opportunities presented by virtual environments.
The Shift to Virtual Communication
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst for the widespread adoption of virtual communication tools among legal professionals, reshaping traditional methods of collaboration and business conduct. Platforms such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Webex swiftly transitioned from being supplementary tools to indispensable resources for remote work, facilitating seamless communication and collaboration across geographical boundaries.
Legal professionals quickly adapted to the virtual landscape, leveraging these platforms to conduct contract drafting negotiations and facilitate deal-making processes. The transition to virtual communication tools revolutionized the way contracts are negotiated, reviewed, and finalized, eliminating the need for in-person meetings and overcoming logistical barriers associated with face-to-face interactions.
Virtual communication tools have democratized contract drafting negotiations, enabling parties to engage in real-time discussions and collaborate on contract management terms regardless of their physical location. Video conferencing features allow participants to communicate effectively, fostering meaningful interactions and reducing the time and costs associated with travel.
Moreover, screen-sharing capabilities have transformed the contract drafting process, allowing parties to review and annotate contract management documents collaboratively. Through shared screens, stakeholders can provide feedback, make revisions, and address concerns in real time, enhancing transparency and expediting the negotiation process.
Electronic signatures have emerged as a key component of virtual contract drafting negotiations, offering a secure and efficient way to execute agreements remotely. Legal professionals can use electronic signature platforms to sign contracts digitally, eliminating the need for physical signatures and postal services. This streamlined approach enhances the efficiency of the contract management execution process, enabling parties to finalize agreements promptly and securely.
Overall, the shift to virtual communication tools has revolutionized contract drafting negotiations, empowering legal professionals to conduct business efficiently and effectively in virtual settings. By embracing virtual communication platforms, legal professionals have overcome geographical barriers, accelerated deal-making processes, and adapted to the demands of a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The Rise of Immersive Technologies
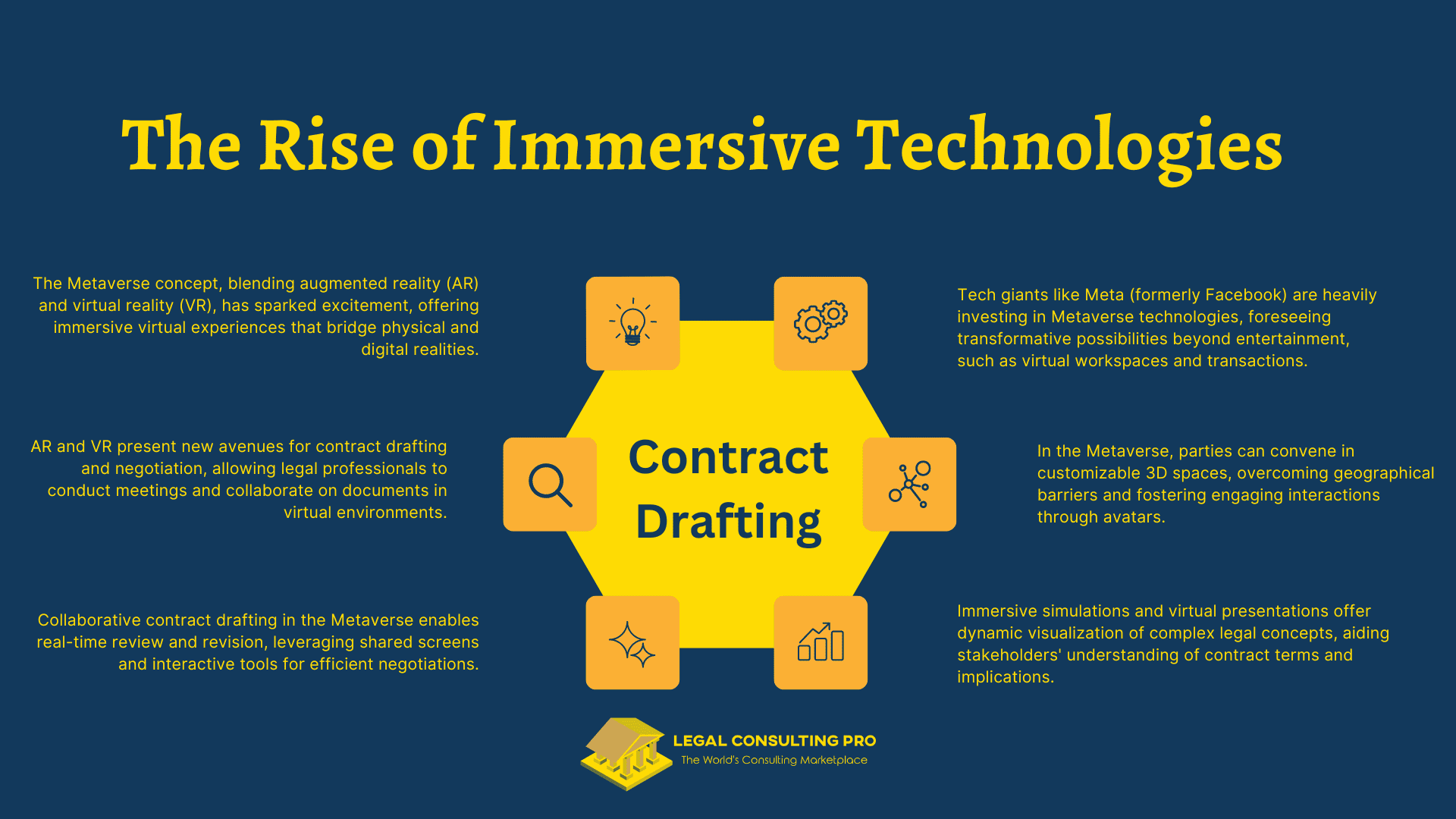
The concept of the Metaverse has ignited excitement and speculation among tech enthusiasts and businesses, heralding a new era of immersive virtual experiences. The Metaverse is envisioned as a virtual shared space that blurs the lines between physical and digital realities, combining elements of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create immersive environments where users can interact, socialize, and conduct business.
Major tech companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) have made significant investments in Metaverse technologies, recognizing the potential for transformative experiences and new business opportunities. Meta’s vision for the Metaverse extends beyond entertainment and social networking, envisioning a future where people can work, collaborate, and transact in immersive virtual environments.
Immersive technologies, including AR and VR, offer unprecedented possibilities for contract drafting and negotiation in the Metaverse. Legal professionals can leverage these technologies to conduct virtual meetings, collaborate on contract documents, and visualize complex concepts in three-dimensional spaces.
In the Metaverse, parties can meet virtually in 3D environments, transcending physical limitations and geographical boundaries. Virtual meeting spaces can be customized to replicate real-world settings or create entirely new environments tailored to the needs of the participants. Through avatars, users can engage in face-to-face interactions, fostering a sense of presence and engagement that rivals traditional in-person meetings.
Collaborating on contract drafting documents in the Metaverse offers unique advantages, allowing parties to work together in real time to review, annotate, and revise contracts in immersive virtual environments. Through shared screens and interactive tools, stakeholders can visualize contract drafting terms, negotiate changes, and reach consensus more efficiently than traditional methods.
Immersive simulations and virtual presentations enable parties to visualize complex concepts and scenarios dynamically and interactively. Legal professionals can use AR and VR technologies to create virtual representations of contract management terms, dispute resolutions, and regulatory frameworks, providing stakeholders with a deeper understanding of the implications and consequences of their decisions.
Adapting Contract Drafting Language for Virtual Environments
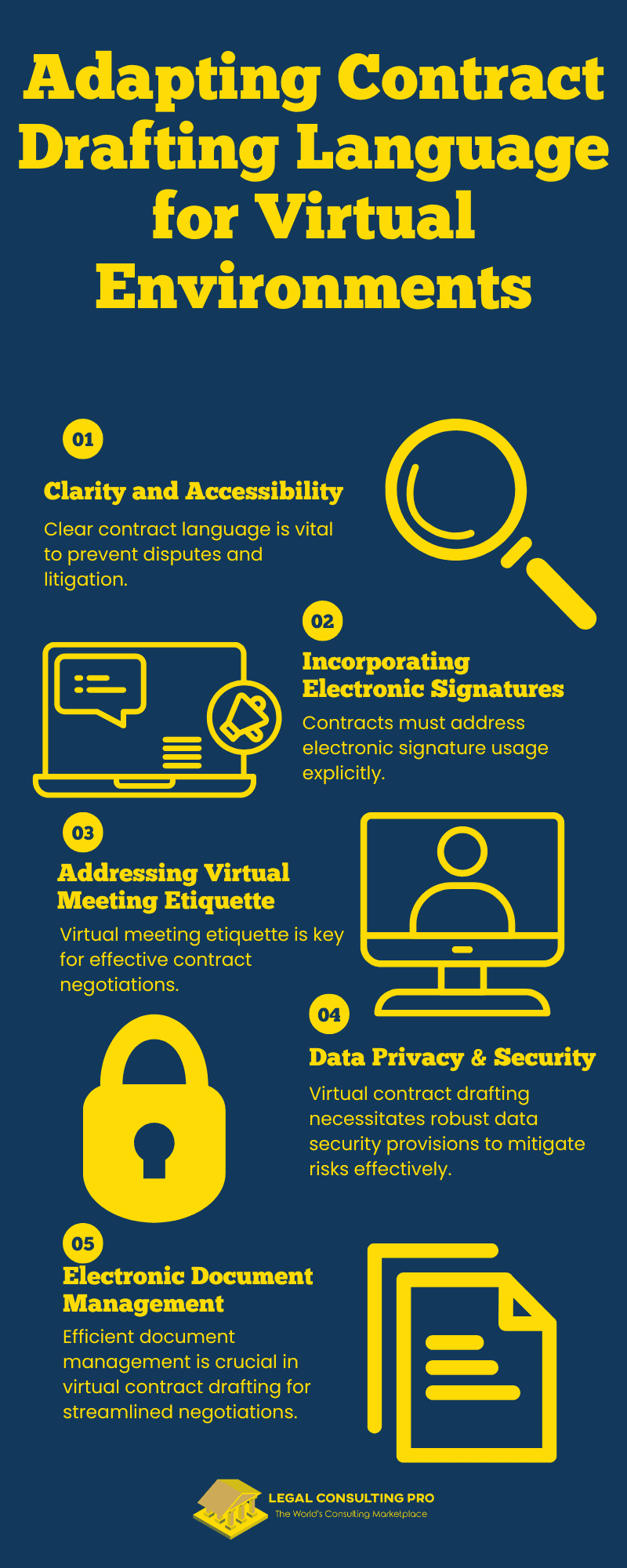
Clarity and Accessibility:
Clarity in contract management language is essential to prevent misunderstandings and ambiguities that could lead to disputes or litigation down the line. The written word carries even greater significance in virtual settings, where face-to-face interactions may be limited. Therefore, legal professionals should strive to articulate contract drafting provisions straightforwardly, leaving no room for interpretation.
To achieve clarity and accessibility in virtual contract drafting, legal professionals can employ several strategies:
- Plain Language: Instead of relying on arcane legal terminology, legal professionals should use plain language that is easily understood by non-lawyers. Plain language conveys information clearly and succinctly, minimizing the risk of confusion or misinterpretation.
- Define Terms: Complex terms or technical jargon should be defined within the contract itself to provide clarity to all parties. Definitions should be clear and concise, ensuring that each term is understood in the same way by all stakeholders.
- Use Examples: Providing examples or hypothetical scenarios can help illustrate the practical implications of contract drafting provisions. This approach enhances understanding and allows parties to grasp the intended meaning of the contractual language more readily.
- Organize Information: Contracts should be logically organized and structured to facilitate comprehension. Clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points can help break down complex information into digestible segments, making it easier for parties to navigate and understand the agreement.
- Seek Feedback: Legal professionals should actively seek feedback from all parties involved in the contract drafting negotiation process to ensure that the language used is clear and accessible. Soliciting input from non-legal stakeholders can help identify potential areas of confusion or ambiguity that need to be addressed.
Incorporating Electronic Signatures:
With the growing prevalence of electronic signatures, it is imperative that contracts explicitly address their use for executing agreements. Contract drafting language should include provisions that not only acknowledge the validity and enforceability of electronic signatures but also ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations governing their use.
Acknowledging the Validity and Enforceability of Electronic Signatures:
In virtual contract drafting, it is essential to explicitly state that electronic signatures are considered valid and legally binding for the execution of agreements. By including provisions that expressly recognize the validity and enforceability of electronic signatures, legal professionals provide clarity and certainty regarding the acceptance of electronic signatures as a valid means of contract drafting execution.
These provisions typically affirm that electronic signatures carry the same legal weight and effect as traditional wet ink signatures. They may also specify that electronic signatures are deemed authentic and attributable to the signatory, ensuring that parties cannot dispute the authenticity of electronically signed contracts.
Compliance with Relevant Laws and Regulations:
In addition to acknowledging the validity of electronic signatures, contracts should include provisions ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations governing their use. Different jurisdictions may have specific requirements or standards for electronic signatures, and contracts need to adhere to these legal requirements to ensure enforceability.
Contract language should reference relevant legislation or statutes governing electronic signatures, such as the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) in the United States or the Electronic Signatures Directive (eIDAS) in the European Union. By incorporating references to these legal frameworks, contracts demonstrate a commitment to compliance with established legal standards for electronic signatures.
Moreover, contracts may include clauses specifying the technical requirements for electronic signatures to ensure security and integrity. These clauses may outline encryption protocols, authentication methods, and audit trails to safeguard against unauthorized access or tampering of electronically signed documents.
Furthermore, contracts may include provisions addressing the revocation or withdrawal of electronic signatures and the procedures for validating electronic signatures in the event of disputes or challenges to their authenticity.
Addressing Virtual Meeting Etiquette:
In virtual contract drafting negotiations, adherence to virtual meeting etiquette is essential to maintaining professionalism and efficiency. Contract management language may include guidelines and protocols for virtual meetings to ensure that all participants can engage in productive discussions and collaboration effectively. These guidelines help establish a framework for communication and behavior, promoting a conducive environment for negotiation and decision-making.
Protocols for Virtual Meetings:
- Muting Microphones: To minimize background noise and ensure clarity during discussions, participants may be required to mute their microphones when not speaking. Contract drafting language may specify this protocol and remind participants to unmute their microphones when they wish to contribute to the conversation.
- Using Chat Features: Virtual meeting platforms often include chat features that allow participants to communicate via text messages. Contract management language may encourage the use of chat features for asking questions, providing feedback, or sharing relevant information during the meeting. Guidelines for using chat features responsibly and respectfully may also be included to prevent distractions and maintain focus.
- Managing Time Effectively: Time management is crucial in virtual meetings to ensure that discussions remain on track and productive. Contract language may include provisions for managing time effectively, such as setting agendas, establishing time limits for each agenda item, and appointing a facilitator or moderator to keep the meeting on schedule.
- Facilitating Productive Discussions: Contract management language may emphasize the importance of active participation and respectful communication in virtual meetings. Participants may be encouraged to listen attentively, avoid interrupting others, and wait for their turn to speak. Guidelines for constructive feedback and conflict resolution may also be included to promote collaborative decision-making and consensus-building.
- Addressing Technical Issues: Virtual meetings may encounter technical issues such as poor internet connectivity, audio or video disruptions, or software glitches. Contract drafting language may include procedures for addressing technical issues, such as providing alternative communication channels or rescheduling the meeting if necessary. Participants may be encouraged to troubleshoot technical problems proactively and seek assistance from technical support if needed.
Data Privacy and Security:
Virtual contract drafting negotiations introduce unique challenges related to data privacy and security, necessitating comprehensive provisions in contract language to address these concerns. Legal professionals must prioritize safeguarding sensitive information exchanged during virtual meetings and document sharing to mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access. Contract drafting language should include provisions that address data protection, confidentiality, and cybersecurity measures, ensuring compliance with relevant data privacy laws and regulations.
Data Protection and Confidentiality:
Contracts should include clauses that outline the parties’ obligations regarding the protection of sensitive information shared during virtual negotiations. These clauses may specify the types of information considered confidential, such as trade secrets, proprietary information, and personally identifiable information (PII). Parties should agree to treat confidential information with the utmost care and take measures to prevent unauthorized disclosure or misuse.
Confidentiality provisions may include obligations to maintain confidentiality, restrictions on sharing confidential information with third parties, and protocols for secure storage and transmission of confidential data. Legal professionals should also consider incorporating non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or confidentiality agreements into the contract management to provide additional legal protections for sensitive information.
Cybersecurity Measures:
In addition to confidentiality provisions, contracts should address cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and cyber threats. Legal professionals should include clauses that require parties to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to safeguard data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
These measures may include encryption protocols, access controls, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to protect against external threats. Contract language may also require regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and employee training programs to ensure ongoing compliance with cybersecurity best practices.
Compliance with Data Privacy Laws and Regulations:
Contract drafting language must adhere to relevant data privacy laws and regulations governing the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data. Depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the data involved, legal professionals may need to consider laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, or industry-specific regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare data.
Contracts should include provisions that require parties to comply with applicable data privacy laws and regulations, including obtaining necessary consent for data processing activities, implementing appropriate data security measures, and providing individuals with rights regarding their data. Legal professionals should also consider including indemnification clauses to allocate liability for data breaches or non-compliance with data privacy laws.
Electronic Document Management:
Effective management of electronic documents is paramount in virtual contract drafting to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and security throughout the negotiation process. Contract language should include provisions that establish protocols for version control, document sharing, and secure storage, thereby enabling all parties involved to access the latest versions of contract management documents and enhancing transparency and accountability in virtual transactions.
Protocols for Version Control:
Contracts should include clauses that outline clear protocols for version control to prevent confusion and ensure that all parties are working with the most up-to-date versions of contract documents. These provisions may specify naming conventions for document versions, such as including the date or a version number in the file name, to facilitate easy identification and tracking of changes.
Additionally, contract management language may establish procedures for documenting revisions, such as maintaining a revision history log or using track changes features in document editing software. By documenting changes systematically, parties can track the evolution of contract drafting negotiations and ensure that all revisions are accurately reflected in the final agreement.
Document Sharing Mechanisms:
Contracts should include provisions that address document-sharing mechanisms to facilitate collaboration and communication among parties involved in the negotiation process. These provisions may specify the preferred method of document sharing, such as using secure file-sharing platforms or cloud-based document management systems.
Contract drafting language should also outline permissions and access controls to restrict access to confidential or sensitive information and ensure that only authorized parties can view or edit contract documents. By implementing appropriate access controls, parties can protect against unauthorized disclosure or tampering of contract documents and maintain data privacy and security.
Secure Storage and Access:
Contracts should include clauses that mandate secure storage and access protocols to protect against data breaches and unauthorized access to contract documents. Contract drafting language may require parties to store contract documents in encrypted or password-protected repositories and implement multi-factor authentication for accessing sensitive information.
Additionally, contracts may specify procedures for securely transferring documents between parties, such as using encrypted email or secure file transfer protocols. Legal professionals should also consider including provisions for data retention and disposal to ensure compliance with applicable data privacy laws and regulations.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms:
In virtual contract drafting, it is essential to anticipate and address potential disputes that may arise from virtual transactions. Contract management language should include provisions that establish clear mechanisms for dispute resolution to facilitate timely and efficient resolution of conflicts. Provisions addressing jurisdiction, governing law, and forum selection are particularly important in virtual environments, where parties may be located in different jurisdictions and conducting business remotely.
Jurisdiction:
Contracts should include clauses that specify the jurisdiction where disputes will be adjudicated in the event of a legal dispute. This jurisdictional clause determines which court or tribunal will have the authority to hear and resolve the dispute. In virtual transactions involving parties from different jurisdictions, determining the appropriate jurisdiction for dispute resolution is crucial to avoid jurisdictional conflicts and ensure the enforceability of judgments.
Governing Law:
Contracts should also specify the governing law that will apply to the interpretation and enforcement of the contract drafting. The governing law clause identifies the legal framework that will govern the rights and obligations of the parties under the contract. Legal professionals should carefully consider the choice of governing law to ensure consistency and predictability in the resolution of disputes, particularly in cross-border transactions.
Forum Selection:
Contracts may include provisions that designate a specific forum or venue for resolving disputes, such as arbitration, mediation, or litigation. The forum selection clause outlines the preferred method of dispute resolution and may specify the rules and procedures governing the chosen forum. Legal professionals should consider the advantages and disadvantages of different dispute resolution mechanisms and tailor forum selection clauses to the unique needs and preferences of the parties involved.
Virtual Dispute Resolution:
In light of the increasing prevalence of virtual transactions, legal professionals should consider the unique challenges of virtual dispute resolution and incorporate provisions that address these challenges into contract management language. Virtual arbitration or online mediation may present logistical, technical, and procedural challenges that require careful consideration and planning. Contracts should include provisions that address issues such as virtual hearings, electronic evidence, and online confidentiality measures to ensure the effectiveness and fairness of virtual dispute resolution processes.
Conclusion
As virtual communication tools and immersive technologies continue to redefine the landscape of contract drafting and negotiation, legal professionals must adapt contract management language to effectively navigate virtual environments. By prioritizing clarity and accessibility, incorporating electronic signature provisions, addressing virtual meeting etiquette, ensuring data privacy and security, implementing electronic document management practices, and specifying dispute resolution mechanisms for virtual transactions, legal professionals can navigate the complexities of virtual contract drafting with confidence. In an era where virtual interactions are becoming increasingly prevalent, adapting contract management language for the rise of virtual contract drafting is essential to fostering effective communication, collaboration, and compliance in virtual transactions.
Similar blogs:
eSports Contract Drafting: Leveling the Playing Field for Players and Sponsors