In today’s digital age, the prevalence of data breaches poses a pervasive threat to individuals’ privacy and security. With vast amounts of personal information stored and exchanged online, the imperative for robust redaction measures to safeguard sensitive data has never been more critical. In this article, we delve into the realm of best practices for redacting personal information, aiming to mitigate the risks of data breaches and uphold individuals’ privacy rights. By harnessing the power of redactions and leveraging litigation support services, organizations can navigate the complexities of a post-privacy scandal world with confidence and integrity.
Understanding Redactions
Redactions is a fundamental process in data protection that involves selectively removing or obscuring sensitive information from documents or digital files to uphold privacy and confidentiality standards. It serves as a critical safeguard against unauthorized access or disclosure of personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, medical records, and other confidential content. By effectively redacting sensitive information, organizations can mitigate the risk of data breaches, protect individuals’ privacy rights, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Different Types of Redactions
Manual Redactions:
- Manual redactions involves the manual identification and removal or covering of sensitive information using traditional tools such as black markers or digital editing software.
- This method offers precise control over the redaction process, allowing individuals to selectively redact specific content based on their discretion.
- However, manual redactions can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error, especially when dealing with large volumes of documents.
Automated Redactions:
- Automated redaction utilizes software tools and algorithms to automatically identify and redact sensitive information from documents or digital files.
- This method offers greater speed, efficiency, and scalability, particularly when dealing with large datasets or repetitive tasks.
- Automated redaction solutions often incorporate advanced features such as pattern recognition, keyword detection, and batch processing to streamline the redaction process.

The Importance of Redactions in Compliance with Privacy Regulations:
Protecting Personal Data:
- Redaction plays a crucial role in protecting individuals’ data from unauthorized access or disclosure, safeguarding their privacy rights, and preventing identity theft or fraud.
- By redacting sensitive information such as social security numbers, addresses, and financial records, organizations ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the data.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
- Privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) impose strict requirements on organizations regarding data protection and privacy.
- Redactions help organizations comply with these regulations by ensuring that sensitive information is appropriately safeguarded and disclosed only to authorized parties.
- Failure to redact sensitive information in compliance with privacy regulations can result in regulatory fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage for organizations.
Legal Implications of Data Breaches
Overview of Legal Frameworks Governing Data Protection:
Data protection laws and regulations are designed to safeguard individuals’ privacy rights and regulate the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information. Key legal frameworks governing data protection include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection law enacted by the European Union (EU) to protect the personal data of individuals within the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). It imposes strict requirements on organizations regarding data processing, consent, transparency, and security.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): The CCPA is a landmark privacy law in the United States, aimed at enhancing consumer privacy rights and increasing transparency and accountability in data practices. It grants California residents certain rights over their personal information and imposes obligations on businesses regarding data collection, disclosure, and consumer rights.
Consequences of Data Breaches:
- Financial Penalties: Data breaches can result in significant financial penalties imposed by regulatory authorities for non-compliance with data protection laws. Under the GDPR, organizations may face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their global annual turnover, whichever is higher, for serious violations of the regulation.
- Reputational Damage: Data breaches can tarnish an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust and loyalty. Public disclosure of a data breach can lead to negative publicity, loss of business opportunities, and long-term damage to brand reputation.
- Legal Liabilities: Data breaches may expose organizations to legal liabilities, including lawsuits from affected individuals, regulatory investigations, and class-action lawsuits. Organizations may be held liable for damages resulting from the breach, such as identity theft, financial loss, or emotional distress suffered by affected individuals.
Role of Litigation Support Services in Addressing Legal Challenges:
- Legal Counsel and Guidance: Litigation support services provide legal counsel and guidance to organizations facing legal challenges post-data breach incidents. They help organizations understand their legal obligations, assess potential liabilities, and develop strategies for mitigating legal risks.
- Evidence Collection and Preservation: Litigation support services assist in collecting, preserving, and analyzing evidence related to the data breach, including forensic analysis of compromised systems, logs, and digital evidence. They ensure that relevant evidence is properly documented and preserved for potential legal proceedings.
- Litigation support services and Case Management: Litigation support services offer assistance in managing legal proceedings related to data breaches, including litigation support, case management, and document review services. They help organizations navigate the complexities of legal proceedings and prepare for court hearings or regulatory investigations.
- Settlement Negotiations and Resolution: Litigation support services facilitate settlement negotiations and resolution of legal disputes arising from data breaches. They work with legal teams to assess settlement options, negotiate favorable terms, and achieve timely resolution of legal matters to minimize financial and reputational damage to the organization.
In summary, data breaches can have significant legal implications for organizations, including financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Litigation support services play a crucial role in helping organizations address legal challenges post-data breach incidents by providing legal counsel, evidence collection, litigation support, and settlement negotiation services. By leveraging the expertise of litigation support services professionals, organizations can effectively manage legal risks and navigate the legal complexities of data breach incidents.

Identifying Personal Information
Common Types of Personal Information: Personal information encompasses a wide range of data that can be used to identify or contact an individual. Some common types of personal information include:
- Names: Full names, nicknames, and aliases.
- Addresses: Residential addresses, mailing addresses, and business addresses.
- Social Security Numbers (SSNs): Unique identification numbers assigned to individuals in the United States for tax purposes.
- Financial Data: Bank account numbers, credit card numbers, and financial transaction details.
- Identification Numbers: Passport numbers, driver’s license numbers, and national identification numbers.
- Contact Information: Phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Health Information: Medical records, health insurance information, and genetic data.
- Biometric Data: Fingerprints, facial recognition data, and iris scans.
- Employment Information: Employment history, job titles, and employer identification numbers.
Challenges in Identifying and Classifying Personal Information Within Large Datasets
Identifying and classifying personal information within large datasets can be challenging due to several factors:
- Volume of Data: Large datasets may contain millions or even billions of records, making it difficult to manually review and classify each piece of information.
- Variety of Data Sources: Personal information may be scattered across various data sources, including databases, documents, emails, and multimedia files, further complicating the identification process.
- Data Complexity: Personal information may exist in different formats, languages, and structures, requiring sophisticated techniques to extract and classify relevant data accurately.
- Data Redundancy: Datasets may contain duplicate or redundant information, leading to inconsistencies and inaccuracies in data classification.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Stringent data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), impose strict requirements on the handling and protection of personal information, necessitating robust data identification and classification processes.
Utilizing Advanced Technology and Algorithms for Efficient Data Categorization
To address the challenges of identifying and classifying personal information within large datasets, organizations can leverage advanced technology and algorithms, including:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP techniques enable computers to understand, interpret, and classify human language data, facilitating the identification of personal information within unstructured text documents.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms can analyze patterns and relationships in data to automatically classify personal information based on predefined criteria, such as keywords, patterns, and context.
- Pattern Recognition: Pattern recognition algorithms can detect and classify personal information by identifying recurring patterns or structures in data, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR technology converts scanned documents and images into machine-readable text, allowing for the extraction and classification of personal information from scanned documents and images.
- Data Masking and Redactions: Data masking and redaction tools can automatically identify and redact sensitive information from documents and digital files, ensuring that personal information is protected from unauthorized access or disclosure.
By leveraging advanced technology and algorithms for efficient data categorization, organizations can overcome the challenges of identifying and classifying personal information within large datasets while ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations and protecting individuals’ privacy rights.
Best Practices for Redacting Personal Information
Prioritize Data Minimization:
- Only collect and retain essential personal information to reduce the risk of exposure in the event of a data breach.
- Regularly review and purge unnecessary data to minimize the scope of sensitive information stored within databases and documents.
Implement Encryption:
- Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access and maintain confidentiality.
- Utilize robust encryption algorithms and key management practices to ensure the security of encrypted data and keys.
Hunter Garnett, Personal Injury Lawyer, Managing Partner, Decatur Personal Injury Lawyers quotes:
Data encryption stands out as a crucial aspect of security compliance for legal outsourcing vendors amidst the surge in electronically stored information (ESI) in legal matters. This method shields sensitive data from unauthorized access by encoding it in a manner that necessitates the correct decryption key for access.
Through the deployment of robust encryption protocols for data during transmission and storage, legal outsourcing vendors can fortify client data against potential security breaches and unauthorized disclosures. Consequently, this proactive measure bolsters client confidentiality and ensures adherence to stringent security standards in managing sensitive legal information.
Secure Data Storage:
- Store personal information in secure, access-controlled environments such as encrypted databases or cloud storage solutions.
- Implement multi-factor authentication and strict access controls to limit access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel.
Train Employees:
- Provide comprehensive training on data protection policies, including redaction procedures, to all employees who handle personal information.
- Educate employees on the importance of handling personal information with care and discretion to minimize the risk of accidental disclosure.
Use Redaction Software:
- Invest in advanced redaction software capable of automatically identifying and redacting personal information from documents and digital files.
- Ensure that the redaction software complies with industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR and CCPA, to ensure the proper handling of sensitive information.
Jonathan Rosenfeld, Owner and Attorney, Rosenfeld Injury Lawyers quotes:
As a lawyer, one unique strategy I’ve found effective for ensuring compliance and mitigating legal risks during the redaction process is implementing automated redaction software. This software utilizes advanced algorithms to identify and redact sensitive information from documents, such as personally identifiable information or privileged communications, while preserving the integrity and readability of the remaining content.
By leveraging automation, legal teams can streamline the redaction process, reduce the risk of human error, and ensure consistent compliance with privacy regulations across large volumes of documents. Additionally, automated redaction software often includes audit trails and reporting features, providing transparency and accountability in the redaction process, which can be invaluable in demonstrating compliance with legal requirements.
Conduct Regular Audits:
- Perform regular audits of data processing activities and redaction practices to identify any potential vulnerabilities or compliance gaps.
- Address any issues or concerns identified during audits promptly to maintain the integrity and effectiveness of redaction processes.
Monitor Redactions Effectiveness:
- Monitor the effectiveness of redaction processes through regular testing and validation to ensure that personal information is properly redacted and protected.
- Implement measures to track and review any incidents or breaches involving redacted information to identify areas for improvement and prevent future occurrences.
Stay Updated on Regulations:
- Stay informed about evolving data privacy regulations and guidelines, such as GDPR, CCPA, and other industry-specific requirements.
- Regularly review and update redaction practices and procedures to align with the latest regulatory standards and best practices in data protection.
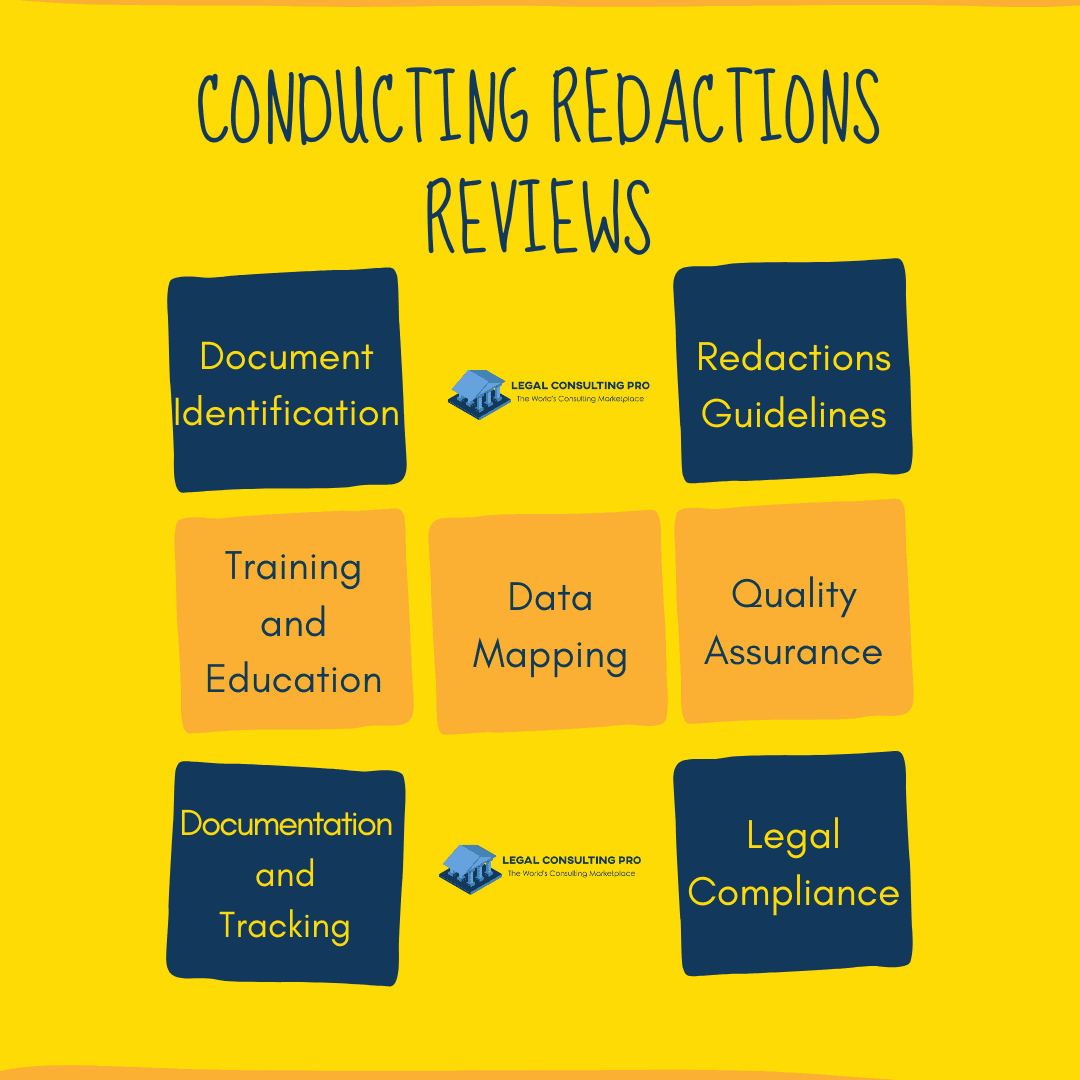
Conducting Redactions Reviews
Establishing a systematic review process is essential to effectively identify and redact personal information from documents and digital files. This process involves several key steps:
- Document Identification: Begin by identifying the documents or files containing personal information that require redaction. This may include contracts, agreements, financial records, emails, and other sensitive materials.
- Data Mapping: Conduct a comprehensive data mapping exercise to understand where personal information is stored and how it is processed within the organization’s systems and databases. This helps to identify the scope of personal data that needs to be redacted.
- Redactions Guidelines: Develop clear and detailed redaction guidelines outlining the types of personal information to be redacted, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, financial data, and other sensitive identifiers. These guidelines should also specify the acceptable methods and techniques for redactions.
- Training and Education: Provide training and education to employees responsible for conducting redaction reviews. Ensure that they understand the redaction guidelines and are proficient in using the necessary tools and software for redaction purposes.
- Review Process: Implement a structured review process to systematically examine documents and identify instances of personal information requiring redactions. This may involve manual review by trained personnel or the use of automated redaction software.
- Quality Assurance: Implement quality assurance measures to ensure the accuracy and completeness of redaction efforts. Conduct random sampling and periodic audits to verify that personal information has been properly redacted according to the established guidelines.
- Documentation and Tracking: Maintain detailed records of redaction activities, including the documents reviewed, redaction decisions made, and any challenges encountered during the process. Track the status of redaction efforts to ensure timely completion and compliance with legal obligations.
- Legal Compliance: Leverage litigation support services to conduct thorough reviews and ensure compliance with legal obligations, such as data privacy laws, regulatory requirements, and court orders. Legal professionals with expertise in data privacy and litigation support services can provide valuable guidance and assistance in navigating complex legal issues related to redactions.
By establishing a systematic review process and leveraging litigation support services, organizations can effectively identify and redact personal information from documents, mitigating the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with legal obligations. This proactive approach helps to safeguard individuals’ privacy rights and maintain trust and confidence in the organization’s handling of sensitive information.
Responding to Data Breaches
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Establish a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines procedures for detecting, assessing, and responding to data breaches. The plan should define roles and responsibilities, establish communication protocols, and include steps for containing the breach, mitigating its impact, and restoring normal operations. Ensure that the plan is regularly reviewed, updated, and tested to maintain its effectiveness.
- Prompt Detection and Assessment: Implement monitoring tools and detection mechanisms to promptly identify potential data breaches. Upon detection, conduct a thorough assessment of the breach to determine the scope, nature, and severity of the incident. Assess the potential impact on affected individuals, systems, and data assets to guide response efforts.
- Notification and Communication: Comply with legal and regulatory requirements regarding data breach notifications to affected individuals, regulatory authorities, and other stakeholders. Provide clear and timely communication about the breach, its impact, and the steps being taken to address it. Transparency and accountability are crucial in maintaining trust and confidence among affected parties.
- Evidence Preservation: Engage litigation support services to assist with evidence preservation and documentation of the data breach. Preserve relevant evidence, such as logs, records, and forensic data, to support investigations, regulatory inquiries, and potential litigation. Adhere to the proper chain of custody procedures to ensure the integrity and admissibility of evidence in legal proceedings.
- Legal Investigations and Compliance: Collaborate with legal counsel and litigation support services to conduct internal investigations into the data breach. Identify the root cause of the breach, assess compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and determine any potential legal liabilities or obligations. Work closely with regulatory authorities and law enforcement agencies as necessary to address compliance issues and legal inquiries.
- Litigation support services: Engage litigation support services to assist with legal proceedings, litigation support, and evidence management in the aftermath of a data breach. Litigation support services professionals can help prepare legal documents, manage discovery processes, and provide expert testimony in court proceedings. Leverage their expertise to navigate complex legal challenges and protect the organization’s interests.
- Remediation and Prevention: Take proactive measures to remediate the effects of the data breach and prevent future incidents. Implement corrective actions to strengthen cybersecurity defenses, enhance data protection measures, and mitigate vulnerabilities that contributed to the breach. Conduct post-incident reviews and lessons-learned exercises to identify areas for improvement and reinforce incident response capabilities.
- Communication and Transparency: Maintain open and transparent communication with affected individuals, stakeholders, and the public throughout the data breach response process. Keep stakeholders informed about the status of the incident, the actions being taken to address it, and any measures they can take to protect themselves. Building trust and credibility through transparent communication is essential in preserving reputation and goodwill amidst a data breach.
Continuous Improvement
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms to solicit input from employees, stakeholders, and external experts regarding redaction practices and incident response procedures. Encourage open communication and constructive feedback to identify areas for improvement and address potential gaps in redaction processes. Actively seek input from individuals involved in data breach response efforts to gather insights and lessons learned from past incidents.
- Lessons Learned Exercises: Conduct regular lessons learned exercises to analyze past data breach incidents and identify opportunities for improvement. Review incident response procedures, redaction practices, and communication protocols to assess their effectiveness and identify areas for enhancement. Document key takeaways, best practices, and areas for improvement to inform future incident response efforts and refine redaction processes.
- Training and Education: Provide ongoing training and education to employees involved in data handling, redactions, and incident response roles. Keep staff informed about emerging threats, evolving regulatory requirements, and best practices in data protection and privacy. Offer specialized training sessions, workshops, and simulations to enhance their skills and knowledge in data security and incident response.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Foster collaboration and information sharing among internal teams, external partners, and industry peers to exchange insights, best practices, and lessons learned in data breach response and redaction practices. Participate in industry forums, conferences, and working groups to stay informed about emerging trends, technologies, and regulatory developments in data protection and privacy. Engage with trusted third-party providers and consultants to access specialized expertise and insights in redaction and incident response.
- Technology Integration and Innovation: Embrace technological advancements and innovative solutions to enhance redaction processes and incident response capabilities. Invest in advanced redaction software, artificial intelligence, and machine learning tools to automate repetitive tasks, improve accuracy, and streamline redaction workflows. Explore opportunities to integrate redaction capabilities into existing systems and platforms to ensure seamless data protection across the organization.
- Regulatory Compliance and Adherence: Stay vigilant about evolving regulatory requirements and compliance obligations in data protection and privacy. Regularly review and update redaction practices to align with changing legal and regulatory landscapes, including updates to data protection laws, industry standards, and best practices. Collaborate with legal counsel and compliance professionals to ensure that redaction processes remain compliant with applicable regulations and guidelines.
- Incident Response Drills and Simulations: Conduct regular incident response drills and simulations to test the effectiveness of redaction processes and incident response procedures. Simulate various data breach scenarios to assess readiness, evaluate response capabilities, and identify areas for improvement. Analyze the outcomes of drills and simulations to refine redaction practices, update incident response plans, and enhance overall preparedness for data breach incidents.
Conclusion
In the wake of escalating data breaches and privacy scandals, effective redaction practices are paramount for protecting personal information and maintaining trust with stakeholders. By adopting best practices for redacting personal information and leveraging litigation support services, organizations can mitigate the risks of data breaches and safeguard individuals’ privacy rights in a post-privacy scandal world. Organizations must prioritize data protection and remain vigilant in the face of evolving threats to ensure the integrity and security of personal information.
Similar blogs:
Beyond Black Boxes: AI and the Future of Redactions in Complex Litigation
From Ransomware to Redaction: Protecting Sensitive Data in the Age of Cyberattacks