The emergence of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we perceive and conduct financial transactions. With the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts, the crypto landscape is rapidly evolving, presenting both opportunities and challenges for businesses and legal professionals. In this article, we delve into the legal framework surrounding smart contract drafting and blockchain transactions, exploring key concepts, challenges, and best practices in navigating the crypto craze.
Understanding Smart Contracts
Smart contracts represent a groundbreaking innovation in the realm of contract law, leveraging blockchain technology to automate and execute contractual agreements without the need for intermediaries. Essentially, smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms and conditions of the agreement are encoded into lines of code that run on a blockchain network. This code governs the execution of the contract, automatically triggering actions when predefined conditions are met.
The decentralized and distributed nature of blockchain technology ensures that smart contracts operate in a tamper-proof and transparent manner. Once deployed on the blockchain, smart contracts are immutable, meaning they cannot be altered or tampered with by any single party. This feature provides a high level of security and trust in the execution of contractual obligations, as the terms of the contract are enforced by the underlying blockchain protocol rather than relying on the trustworthiness of third-party intermediaries.
Smart contracts offer a plethora of benefits over traditional paper-based contracts. Firstly, they enable the automation of complex business processes, streamlining workflows, and reducing the need for manual intervention. This automation leads to increased efficiency, as smart contracts can execute transactions and enforce agreements in real-time, without human intervention.
Secondly, smart contracts enhance transparency by providing a transparent and auditable record of all transactions and contract execution on the blockchain. This transparency fosters trust among parties by ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the same information and can verify the integrity of the contract execution process.
Additionally, smart contracts offer cost savings by eliminating the need for intermediaries such as lawyers, brokers, or escrow agents to facilitate and enforce agreements. By automating contract execution, smart contracts reduce overhead costs associated with manual contract management and enforcement, resulting in significant cost savings for businesses.
However, despite their numerous benefits, the implementation of smart contracts requires careful consideration of legal and regulatory requirements. Since smart contracts operate on blockchain networks that may span multiple jurisdictions, legal professionals must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Legal considerations for smart contract implementation include contract formation, validity, enforceability, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Legal professionals must ensure that the terms and conditions encoded in smart contracts accurately reflect the intentions of the parties and comply with relevant legal requirements.
Moreover, legal frameworks for smart contracts are still evolving, with regulators grappling with issues such as jurisdictional ambiguity, consumer protection, and data privacy concerns. As such, legal professionals must stay abreast of regulatory developments and adapt smart contract drafting practices to ensure compliance with emerging legal standards.
Legal Implications of Smart Contract Drafting
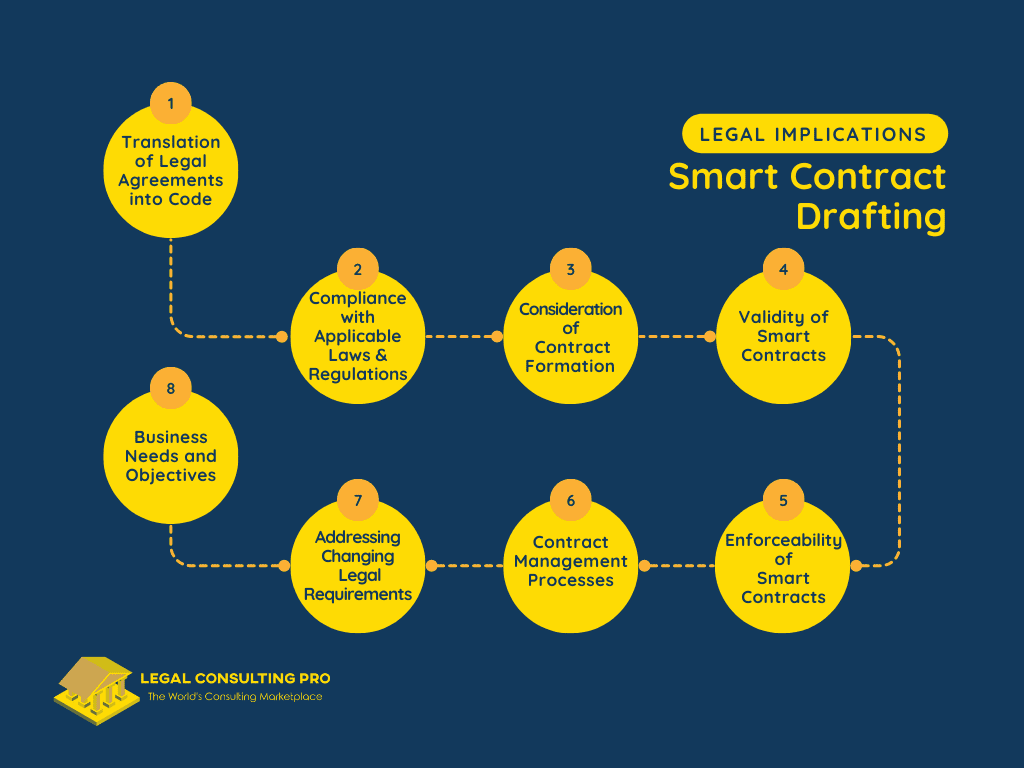
Contract drafting and management for smart contracts involve translating legal agreements into code, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations, and establishing processes for ongoing monitoring, updating, and enforcement. Legal professionals play a crucial role in ensuring that smart contracts are legally sound, enforceable, and aligned with the business objectives of the parties involved.
- Translation of Legal Agreements into Code: Contract drafting for smart contracts entails the translation of traditional legal agreements into code that can be executed on a blockchain network. This involves converting legal language and contractual terms into machine-readable code that governs the behavior of the smart contract.
- Compliance with Applicable Laws and Regulations: Legal professionals must ensure that smart contracts comply with relevant laws and regulations governing contract formation and execution. This includes adherence to contract law principles, as well as compliance with specific legal requirements applicable to smart contracts, such as electronic signature laws, data protection regulations, and consumer protection laws.
- Consideration of Contract Formation: Smart contract drafting requires consideration of the legal principles governing contract formation, such as offer, acceptance, and consideration. Legal professionals must ensure that the terms and conditions encoded in the smart contract accurately reflect the intentions of the parties and satisfy the requirements for a valid contract formation.
- Validity of Smart Contracts: Legal professionals must assess the validity of smart contracts to ensure that they are legally enforceable. This involves verifying that the smart contract complies with legal formalities, such as the requirement for mutual assent, capacity to contract, and lawful purpose. Additionally, legal professionals must consider any statutory or common law requirements that may impact the validity of the smart contract.
- Enforceability of Smart Contracts: Smart contracts must be drafted in a manner that ensures their enforceability in the event of a dispute. This includes incorporating dispute resolution mechanisms, such as arbitration or mediation clauses, into the smart contract code. Legal professionals must also consider the jurisdictional implications of smart contract enforcement and ensure that the terms of the smart contract are enforceable under applicable laws.
- Contract Management Processes: Contract management for smart contracts involves ongoing monitoring, updating, and enforcement to address changing legal requirements and business needs. Legal professionals must establish processes for monitoring the performance of smart contracts, updating contract terms as needed, and enforcing contractual obligations in accordance with legal requirements.
- Addressing Changing Legal Requirements: Legal professionals must stay abreast of changing legal requirements and regulations that may impact the performance and enforceability of smart contracts. This includes monitoring regulatory developments related to blockchain technology, smart contracts, and cryptocurrency transactions, and updating smart contract terms to ensure compliance with emerging legal standards.
- Business Needs and Objectives: Contract management processes for smart contracts should be aligned with the business needs and objectives of the parties involved. Legal professionals must work closely with business stakeholders to understand their requirements and objectives and tailor smart contract terms and management processes accordingly.
Challenges: Smart Contract Drafting
- Regulatory Compliance: One of the primary challenges in smart contract drafting is navigating regulatory compliance in a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape. Depending on the nature of the transaction and the jurisdictions involved, smart contracts may be subject to securities, tax, consumer protection, anti-money laundering (AML), and other regulatory requirements. Legal professionals must stay abreast of regulatory developments and tailor smart contract terms to ensure compliance with relevant laws.
- Security and Privacy Considerations: Security and privacy are paramount in blockchain transactions, given the immutable and transparent nature of distributed ledger technology. Smart contract drafting should include provisions for data protection, confidentiality, and cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive information and mitigate the risk of security breaches or data leaks. Contract management practices should also incorporate regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
- Risk Management: Effective risk management strategies are essential for mitigating legal and financial risks associated with smart contract drafting and blockchain transactions. Legal professionals should conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential risks, such as coding errors, regulatory non-compliance, contractual disputes, and market volatility. Contract management processes should include risk mitigation measures, such as insurance coverage, dispute resolution mechanisms, and contingency plans for handling unforeseen events.
- Enforcement and Dispute Resolution: Enforcing smart contracts and resolving disputes in blockchain transactions pose unique challenges due to the decentralized and pseudonymous nature of blockchain networks. Legal frameworks for contract enforcement and dispute resolution may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the governing law specified in the smart contract. Contract drafting should include clear provisions for dispute resolution mechanisms, such as arbitration, mediation, or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), to facilitate the timely and effective resolution of disputes.
Best Practices for Smart Contract Drafting
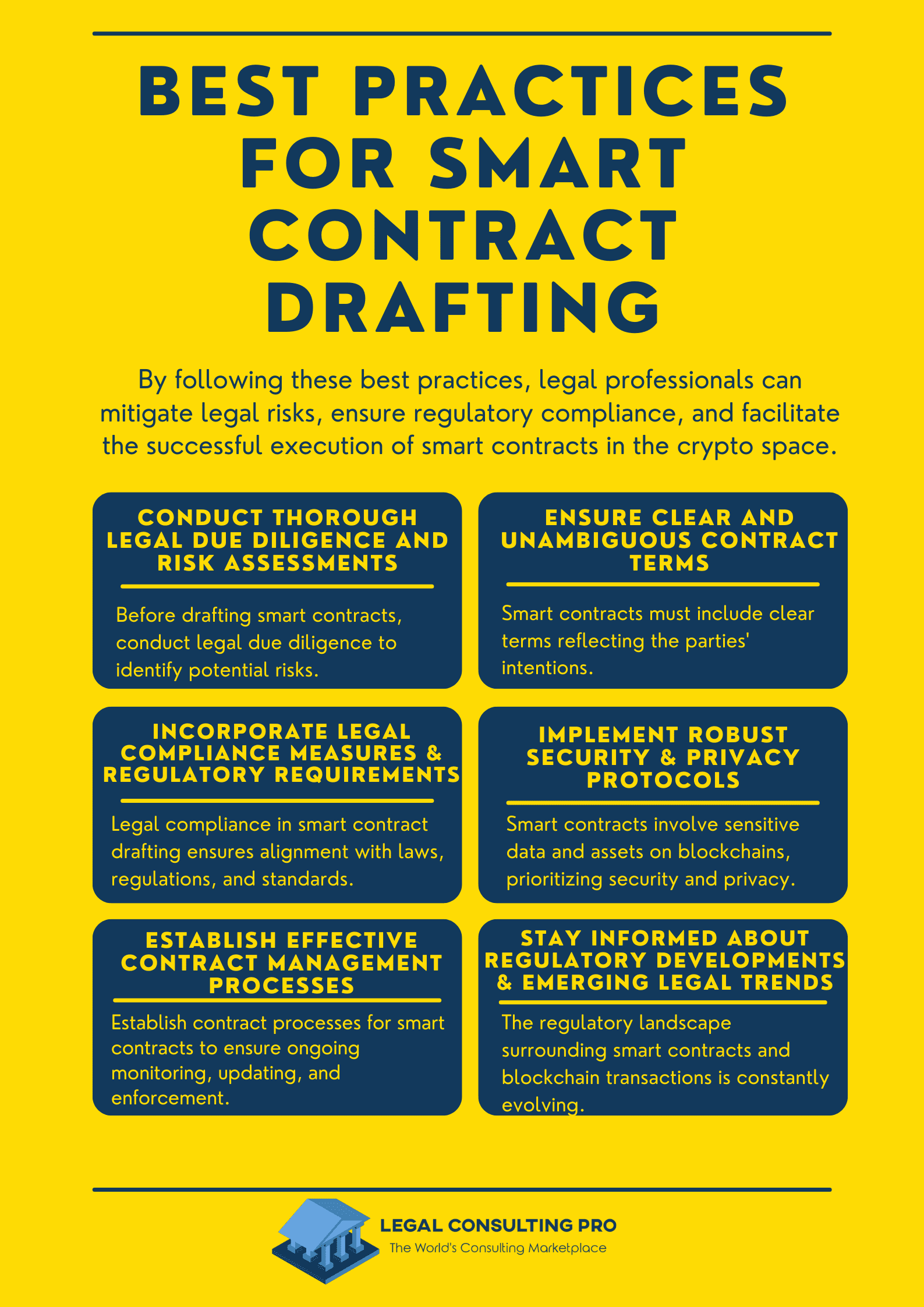
To navigate the legal complexities of smart contract drafting and blockchain transactions effectively, legal professionals should adhere to best practices such as conducting thorough legal due diligence, ensuring clear contract terms, incorporating legal compliance measures, implementing robust security protocols, establishing effective contract management processes, and staying informed about regulatory developments. By following these best practices, legal professionals can mitigate legal risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and facilitate the successful execution of smart contracts in the crypto space.
- Conduct Thorough Legal Due Diligence and Risk Assessments: Before drafting smart contracts, legal professionals should conduct comprehensive legal due diligence and risk assessments to identify potential legal issues, regulatory requirements, and risks associated with the proposed transaction. This includes assessing the legal validity and enforceability of the smart contract terms, as well as identifying potential legal challenges or disputes that may arise during contract execution.
- Ensure Clear and Unambiguous Contract Terms: Smart contracts should incorporate clear and unambiguous terms and conditions that accurately reflect the intentions of the parties. Legal professionals should work closely with stakeholders to define the rights, obligations, and responsibilities of each party in the smart contract. This includes specifying the scope of the agreement, defining key terms, and outlining the conditions for contract execution and performance.
- Incorporate Legal Compliance Measures and Regulatory Requirements: Legal compliance is essential in smart contract drafting to ensure that the terms and conditions of the contract comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. Legal professionals should incorporate legal compliance measures, such as know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements, data protection regulations, and consumer protection laws, into smart contract terms to mitigate legal risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Implement Robust Security and Privacy Protocols: Smart contracts often involve the exchange of sensitive information and assets on blockchain networks, making security and privacy paramount. Legal professionals should implement robust security and privacy protocols to protect sensitive information and mitigate cybersecurity risks. This includes encryption techniques, access controls, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in smart contract systems.
- Establish Effective Contract Management Processes: Contract management processes for smart contracts should be established to ensure ongoing monitoring, updating, and enforcement of contract terms. Legal professionals should develop procedures for monitoring the performance of smart contracts, updating contract terms as needed, and enforcing contractual obligations in accordance with legal requirements. This includes establishing clear communication channels, escalation procedures, and dispute-resolution mechanisms to address issues that may arise during contract execution.
- Stay Informed about Regulatory Developments and Emerging Legal Trends: The regulatory landscape surrounding smart contracts and blockchain transactions is constantly evolving. Legal professionals should stay informed about regulatory developments, changes in legislation, and emerging legal trends in the crypto space to adapt smart contract drafting practices accordingly. This includes participating in industry forums, attending legal conferences, and engaging with regulatory authorities to stay abreast of legal developments and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Conclusion
The crypto craze presents exciting opportunities for innovation and growth, but it also brings legal and regulatory challenges that must be carefully navigated. Smart contract drafting and blockchain transactions require a nuanced understanding of legal principles, regulatory frameworks, and technological complexities. By adhering to best practices and staying informed about legal developments, legal professionals can effectively navigate the legal landscape of the crypto industry and help their clients leverage the transformative potential of blockchain technology.
Similar Blogs:
Influencer Marketing Contract Drafting: Legal Pitfalls and Hidden Gems for Brands